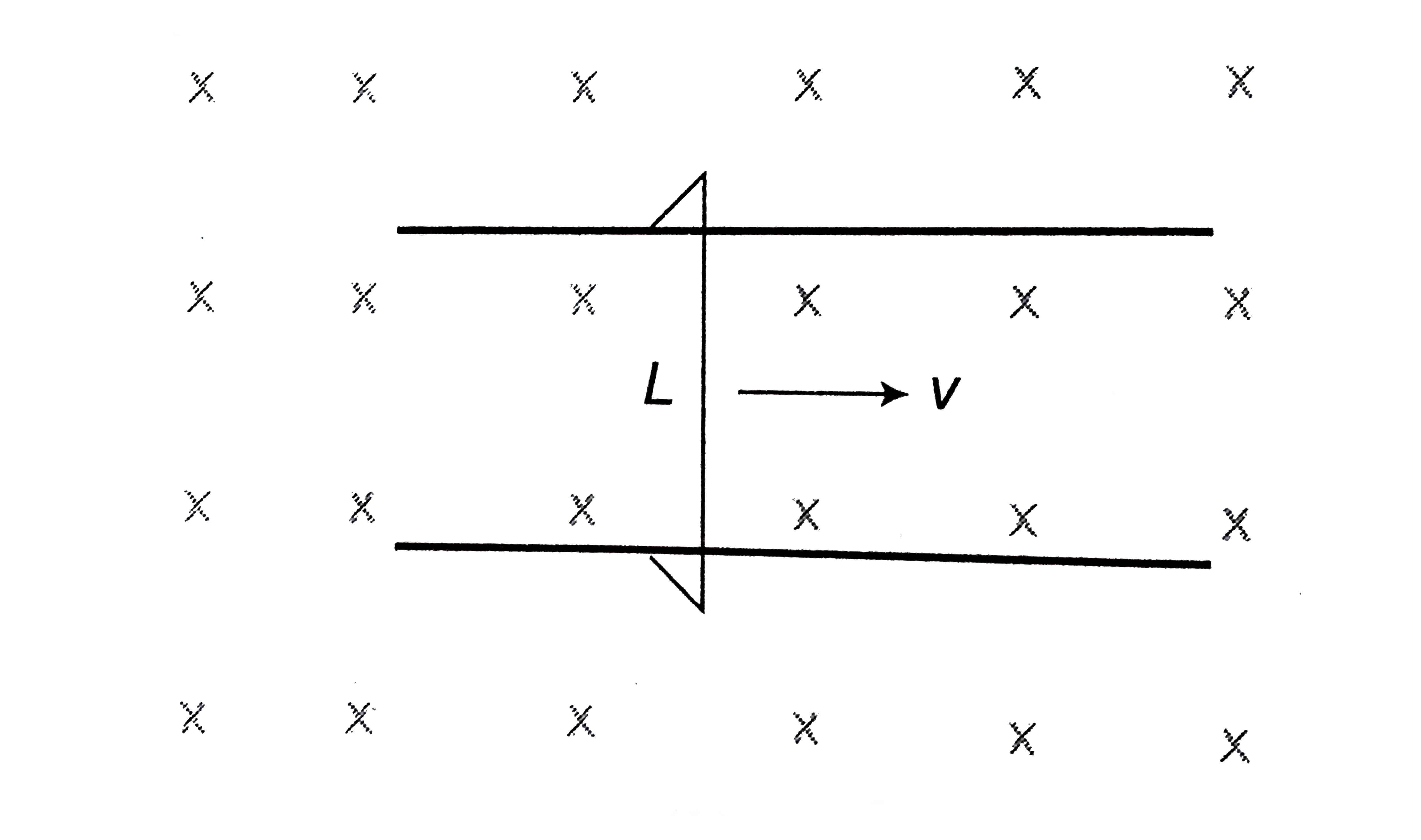
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-EXERCISES
- A conducing rod of length l is falling with a velocity v perpendicular...
Text Solution
|
- A square metal wire loop of side 10 cm and resistance 1 ohm is moved w...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed a...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mas m is moving with constant velocity v(0) in a perp...
Text Solution
|
- A conductor PQ , with PQ=r , moves with a velocity v in a uniform magn...
Text Solution
|
- The wings of an aeroplane are I0m apart. The plane is moving horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- The two rails of a railway track, insulated from each other and the gr...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of the earth's magnetic field at a place is B(0) and an...
Text Solution
|
- In the precious question, if the conductor lies east-west and the move...
Text Solution
|
- The two ends of a horizontal conducting rod of length l are joined to ...
Text Solution
|
- A player with 3 meter long iron rod runs toward east with a speed of ...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of the earth's magnetic field at the north pole is B(0) ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length 10cm translates in a direction making an angle of 60^...
Text Solution
|
- The loop shown moves with a velocity v in a uniform magnetic field of ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic square loop ABCD is moving in its own plane with velocity v...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting square loop of side l and resistance R moves in its plane...
Text Solution
|
- A right angled triangle abc, made from a metallic wire, moves at a uni...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop ABCD of edge a moves to the right with a velocity v para...
Text Solution
|
- In the previous question, in position I of the loop (i) The induced ...
Text Solution
|
- Shown a square loop of side 5 cm beign moved towards right at a consta...
Text Solution
|