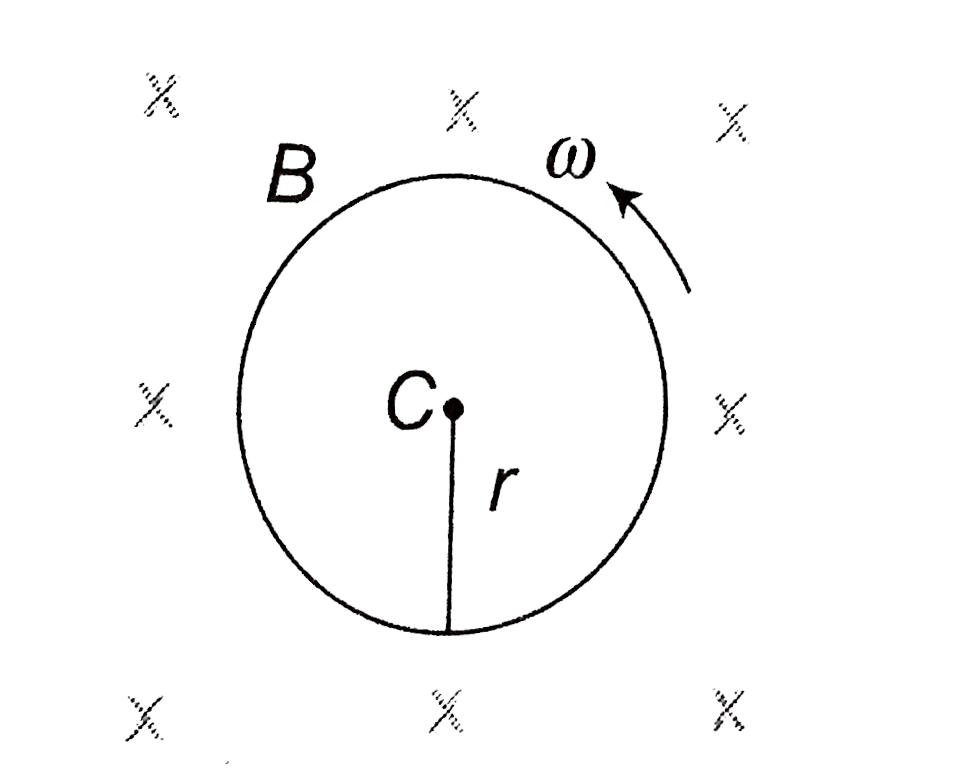
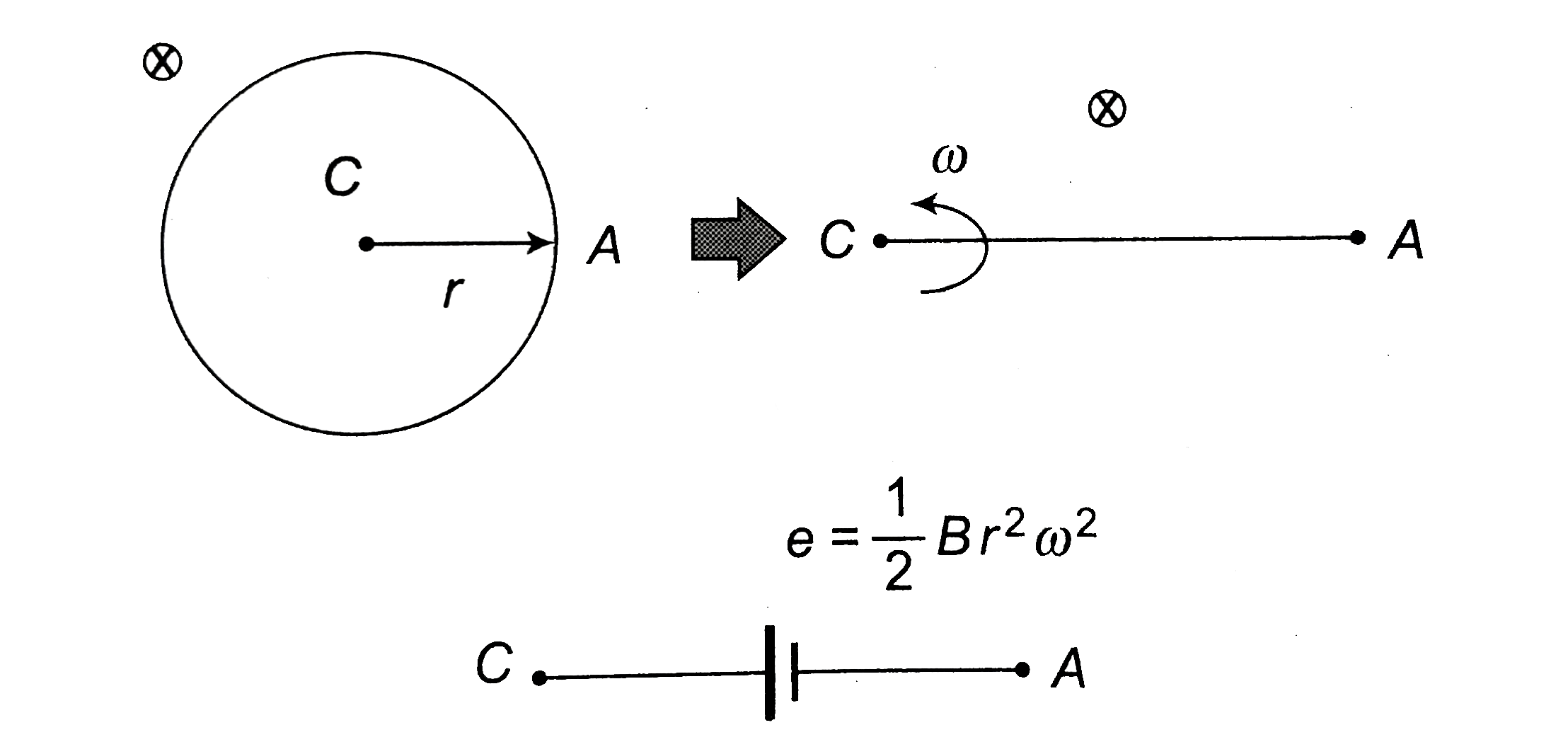
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-EXERCISES
- A metal conductor of length 1m rotates vertically about one of its end...
Text Solution
|
- A metal rod of resistance R is fixed along a diameter o fa conducting ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting disc of radius r spins about its axis an angular velocity...
Text Solution
|
- Three indential rings move with same speed on a horizontal magnetic fi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform but time-varying magnetic field B(t) exists in a circular re...
Text Solution
|
- The inductance of a coil is proportional to
Text Solution
|
- When the number of turns and the length of the solenoid are doubled ke...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid has 500 turns. When a current of 2A is passed through ...
Text Solution
|
- A coil is wound as a transformer of rectangular cross section. If all ...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid of N turns has a self-induced L and area of cross-sect...
Text Solution
|
- The SI unit of inductance, the henry can be written as
Text Solution
|
- Pure inductance of 3.0 H is connected as shown below. The equivalent i...
Text Solution
|
- The equivalent inductance of two inductors is 2.4 H when connected in ...
Text Solution
|
- When the current in a coil changes from 8A to 2A in 3xx10^(-2)s , th e...
Text Solution
|
- A current of 2A flowing through a coil of 100 truns give rise to a nag...
Text Solution
|
- L,C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance an...
Text Solution
|
- If I=5A and decreasing at a rate of 10^(2)(A//sec) , then V(B)-V(A)
Text Solution
|
- In the previous question, if the direction of I is reversed, V(B)-V(A)...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating current I in an inductance coil varies with time t acco...
Text Solution
|
- The current i in a coil varies with time as shown in the figure. The v...
Text Solution
|