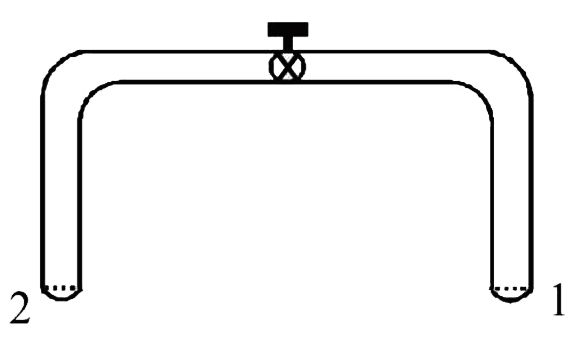
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise 5 B (Multiple correct answers)|2 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise 5 B (Comprehension)|5 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise 5 A (Previous year Questions)|29 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-V B|19 VideosERROR AND MEASUREMENT
ALLEN|Exercise Part-2(Exercise-2)(B)|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-ELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS-Exercise 5 B (MCQ)
- Water from a tap emerges vertically downwards with an initial spped of...
Text Solution
|
- A given quantity of a ideal gas is at pressure P and absolute tempera...
Text Solution
|
- A closed compartment containing gas is moving with some acceleration i...
Text Solution
|
- A large open tank has two holes in the wall. One is a square hole of s...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical portion of radius R is removed from the bottom of a cy...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden block, with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as show...
Text Solution
|
- The adjacent graph shows the estension (Deltal) of a wire of length 1m...
Text Solution
|
- The presssure of a medium is changed from 1.01xx10^(5) Pa to 1.165xx...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled in a cylindrical container to a height of 3m. The rati...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled up to a height h in a beaker of radius R as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- A glass tube of uniform internal radius(r) has a valve separating the ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a horizontal thick copper wire of length 2L and radius 2R i...
Text Solution
|
- A glass capillary tube is of the shape of a truncated cone with an ape...
Text Solution
|