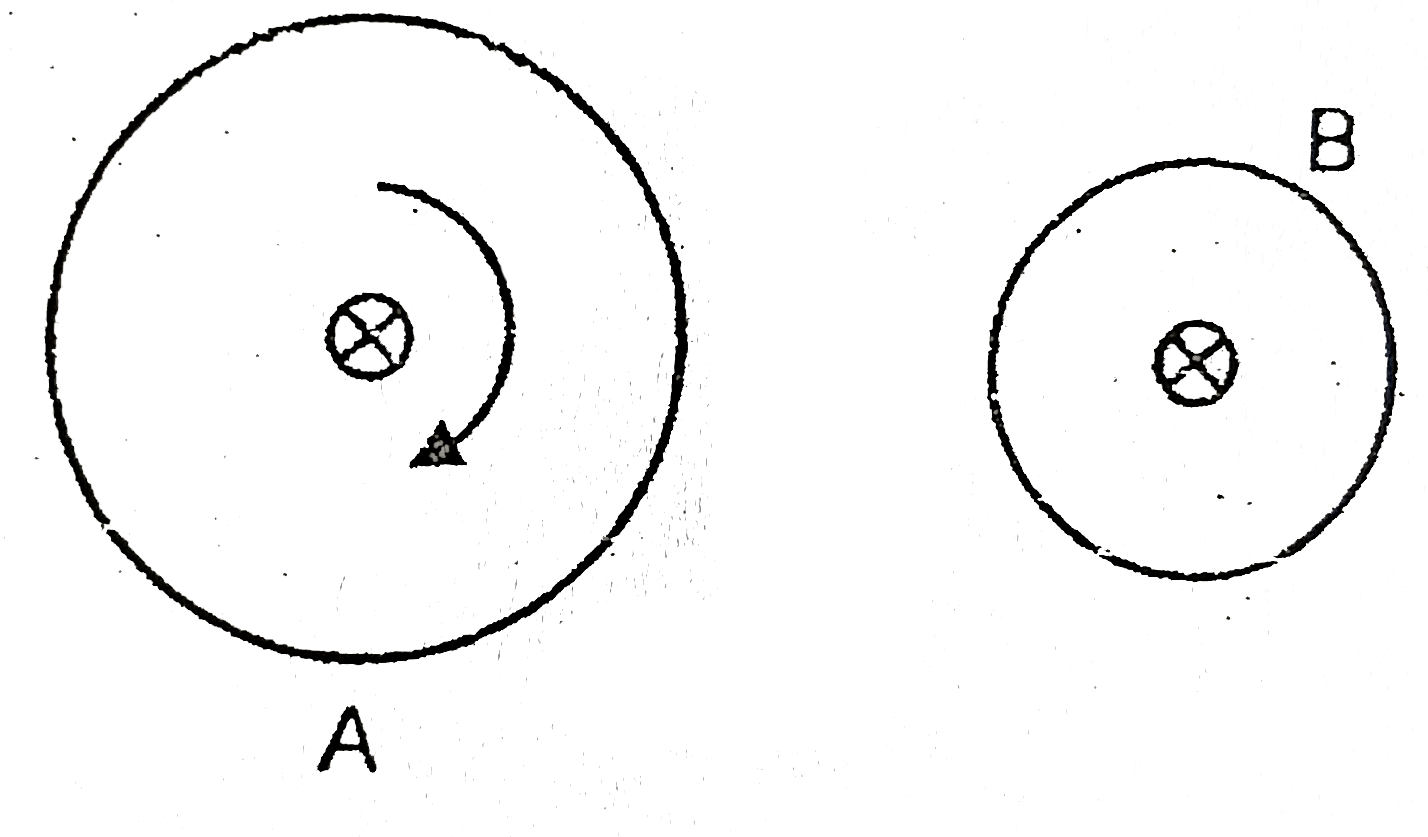A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two disks A and B are free to rotate about their respective vertical ...
Text Solution
|
- An annular circular brass disk of inner radius 'r' and outer radius 'R...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting disk of radius R is rotating about its own axis with ...
Text Solution
|
- Two disks A and B are free to rotate about their respective vertical ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disk of mass 300kg is rotating freely about a vertical axis ...
Text Solution
|
- Two discs A and B are in contact and rotating with angular velocity wi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disk of mass 100 kg and radius 2 m is rotating at 1 rad/s ...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal disk is rotating with angular velocity omega about a vert...
Text Solution
|
- About disks with equal inertial torque, about the axis perpendicular t...
Text Solution
|