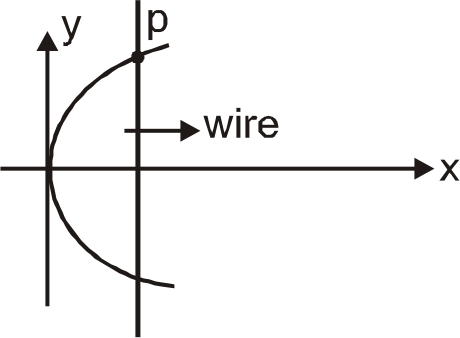
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise TRUE/FALSE|2 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 25|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp23|8 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|54 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp 24
- System is shown in the figure. Velocity of sphere A is 9 (m)/(s). Find...
Text Solution
|
- A boy and a block, both of same mass, are suspended at the same horizo...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown neglecting friction and mass of pulley, what is th...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is bent in a parabolic shape followed by equation x=4y^(2) cons...
Text Solution
|
- Blocks of mass M(1) and M(2) are connected by a cord which passes over...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, at the free end of the light string, a force F is sppli...
Text Solution
|