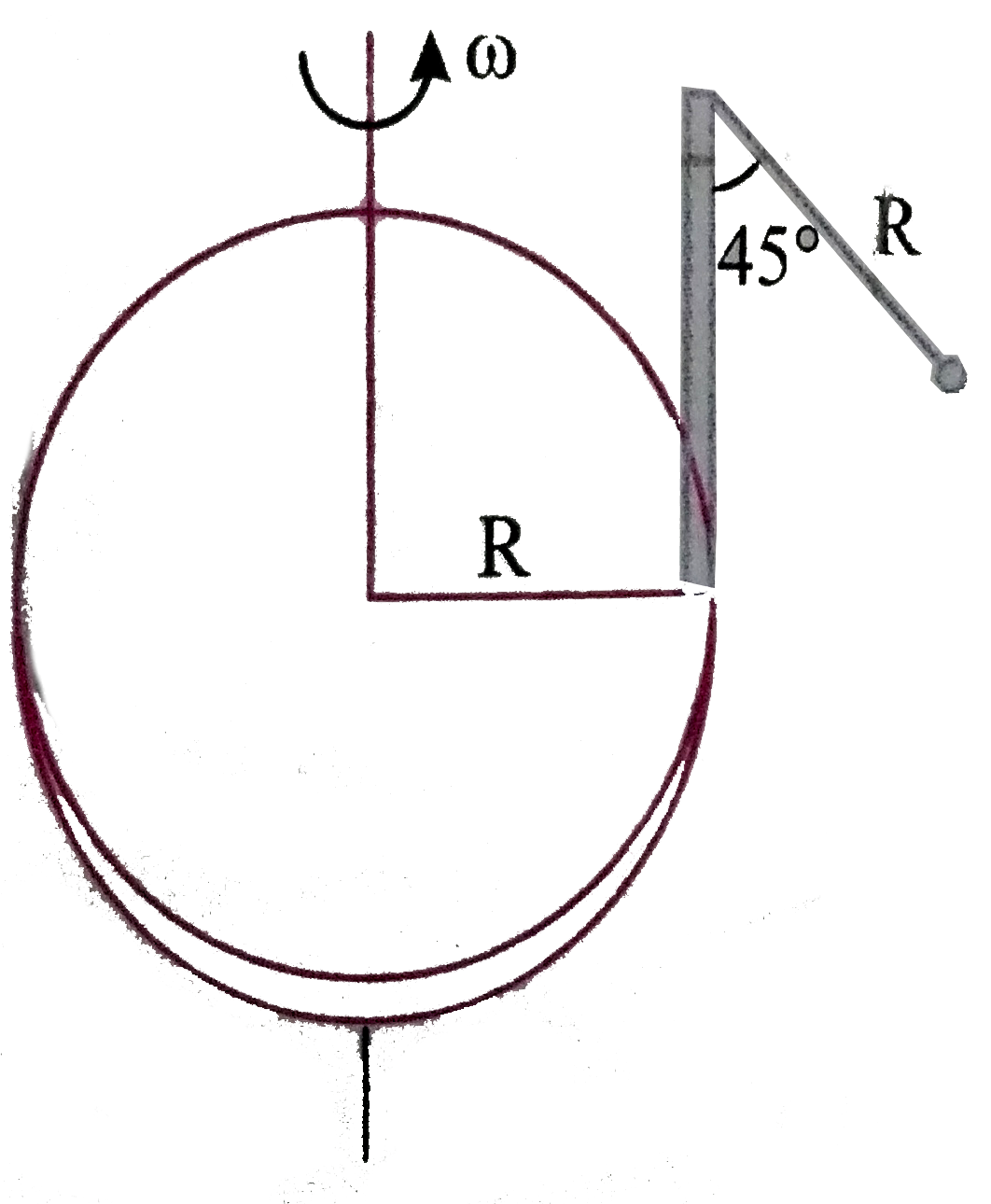
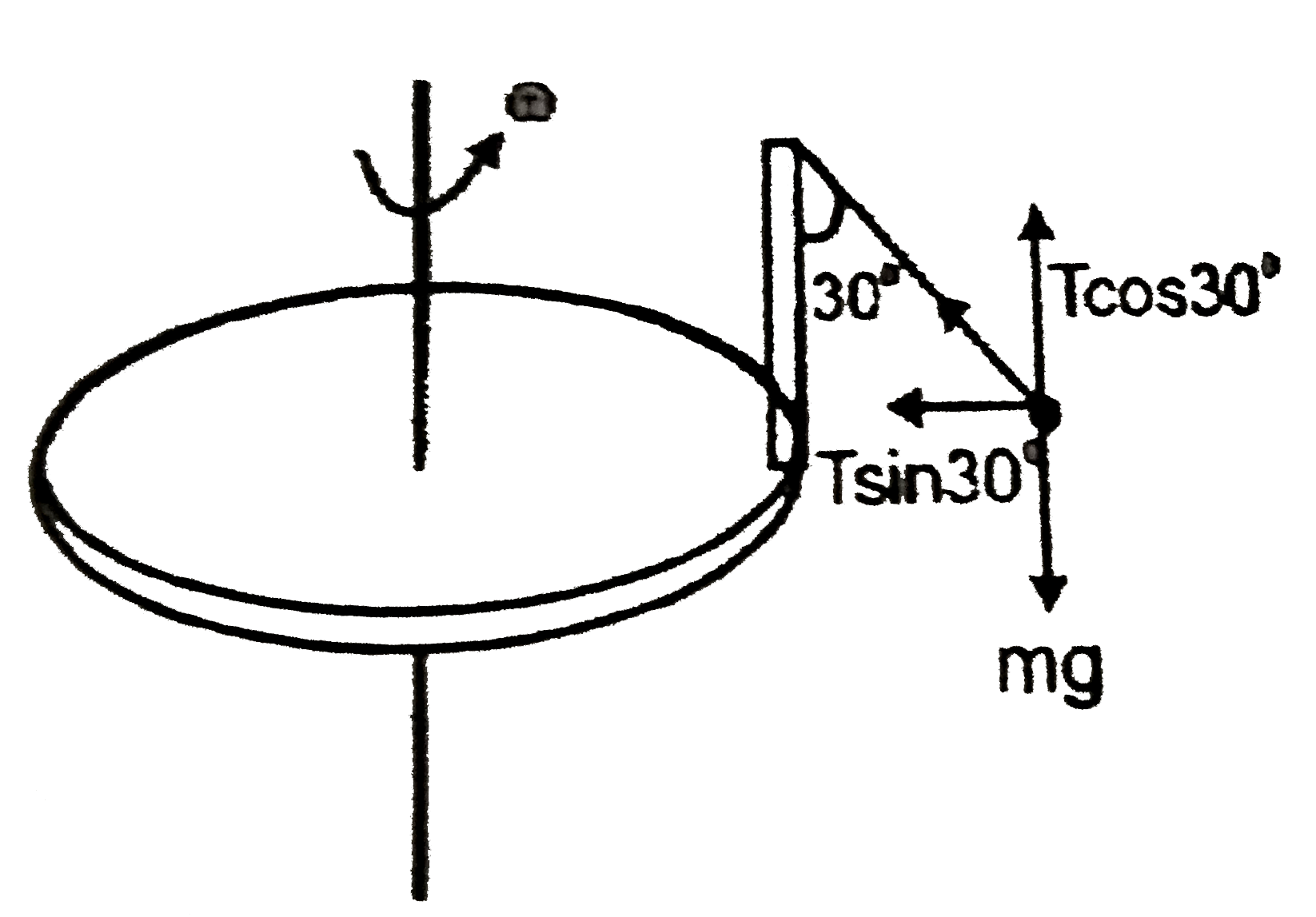
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 43|11 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 44|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 41|7 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|54 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp 42
- A block of mass m starts at rest at height on a frictionless inclined ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, block A is released from rest when the spring is its na...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving in a circle of radius r with speed v as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy function associated with the force vecF=4xyhati+2...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R has a light pole fixed perpendicular to the disc at...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are placed in contact with each oth...
Text Solution
|
- A car initially travelling eastwards turns noth by travelling in a qua...
Text Solution
|