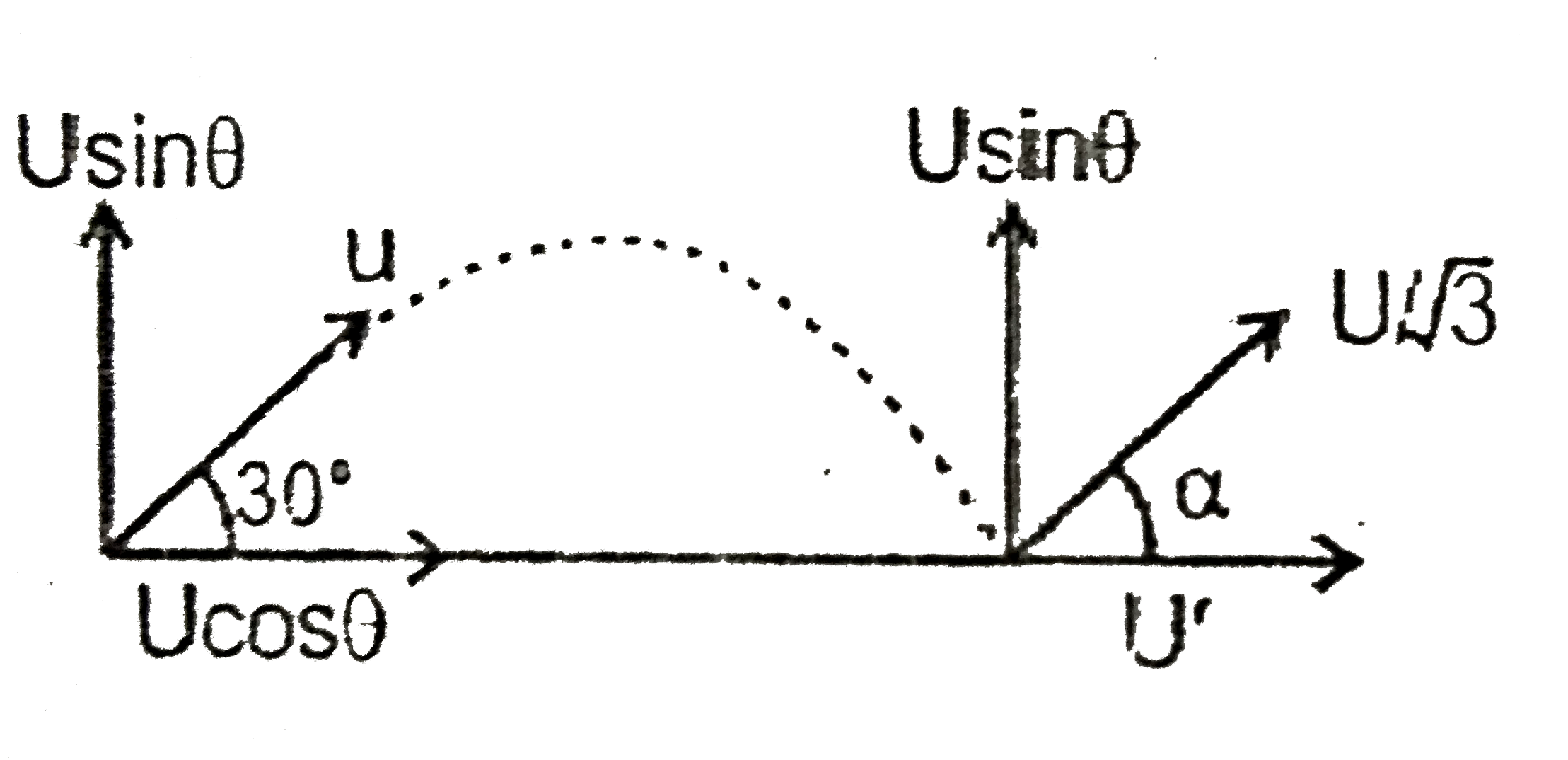
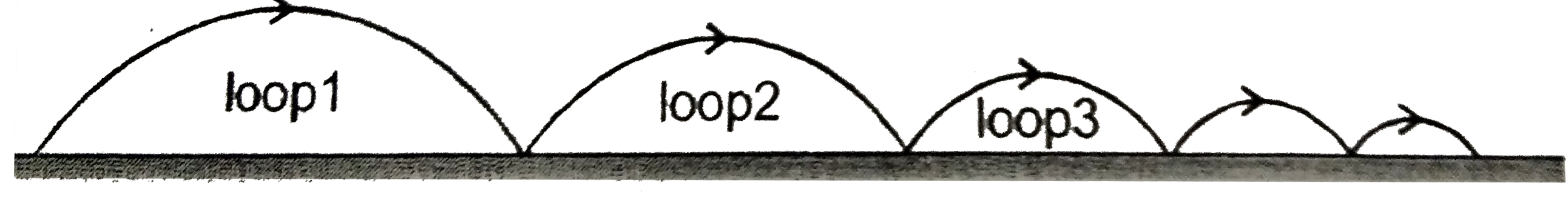A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A ball is projected on a very long floor. There may be two conditions ...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical balls, ball I, ball II and ball III are placed on a sm...
Text Solution
|
- A ball hits the floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In th...
Text Solution
|
- A ball, rolling purely on a horizontal floor with centre's speed v , h...
Text Solution
|
- In the previous problem , if the horizontal surface is rough with fric...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected on a very long floor. There may be two conditions ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected on a very long floor. There may be two conditions ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected on a very long floor. There may be two conditions ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball rebounds after colliding with the floor, then in case of inelas...
Text Solution
|