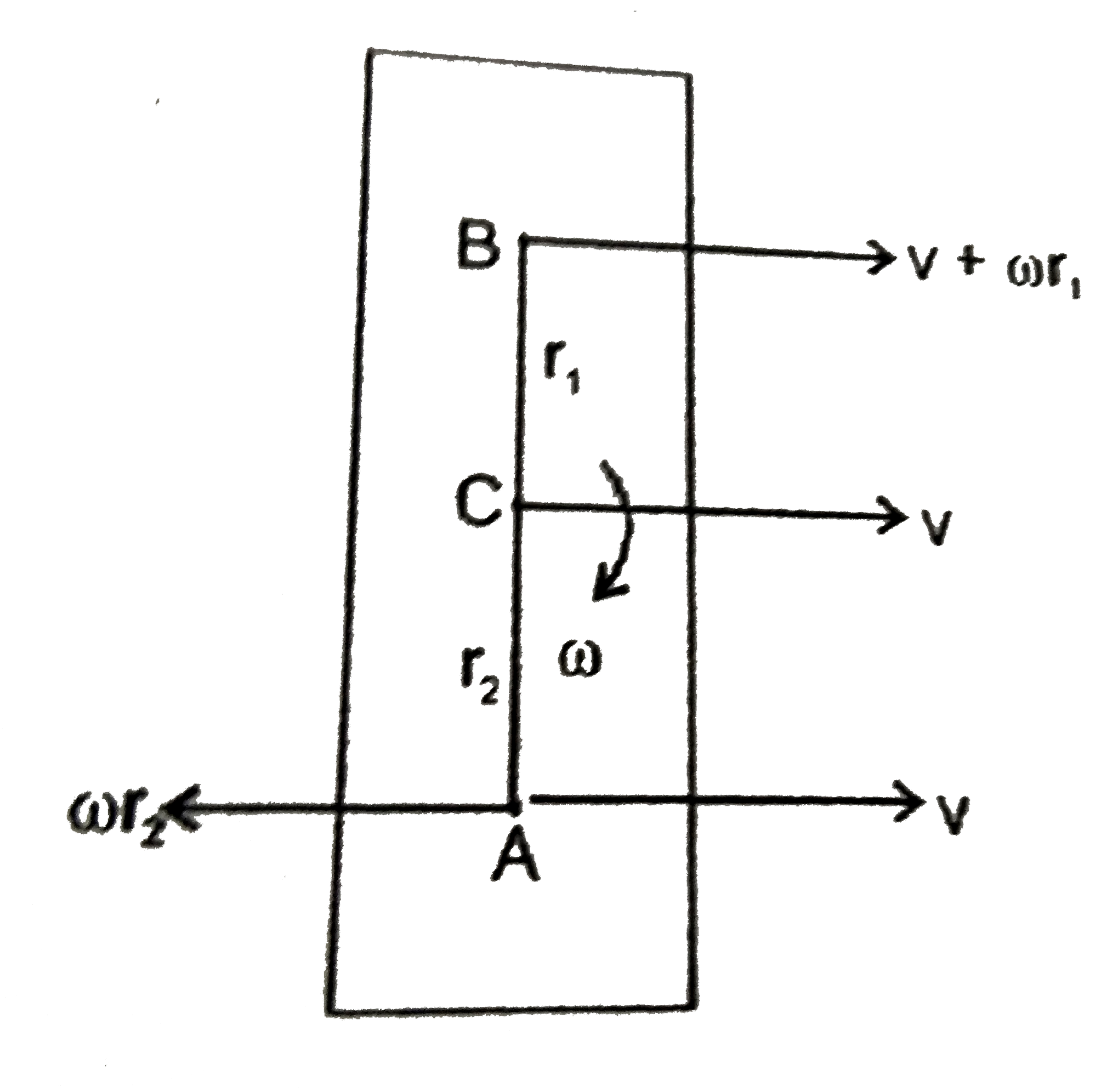
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP 62|4 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 63|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 60|5 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|54 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp61
- A ball collides elastically with a massive wall moving towards it with...
Text Solution
|
- A block attached to a spring, pulled by a constant horizontal force, i...
Text Solution
|
- A planar object made up of a uniform square plate and four semicircula...
Text Solution
|
- The angular velocity of a rigid body about any point of that body is s...
Text Solution
|
- On a smooth carrom board. A coin located at (4,6) is moving in negativ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of mass m and length l hanges on a thread and touches ...
Text Solution
|