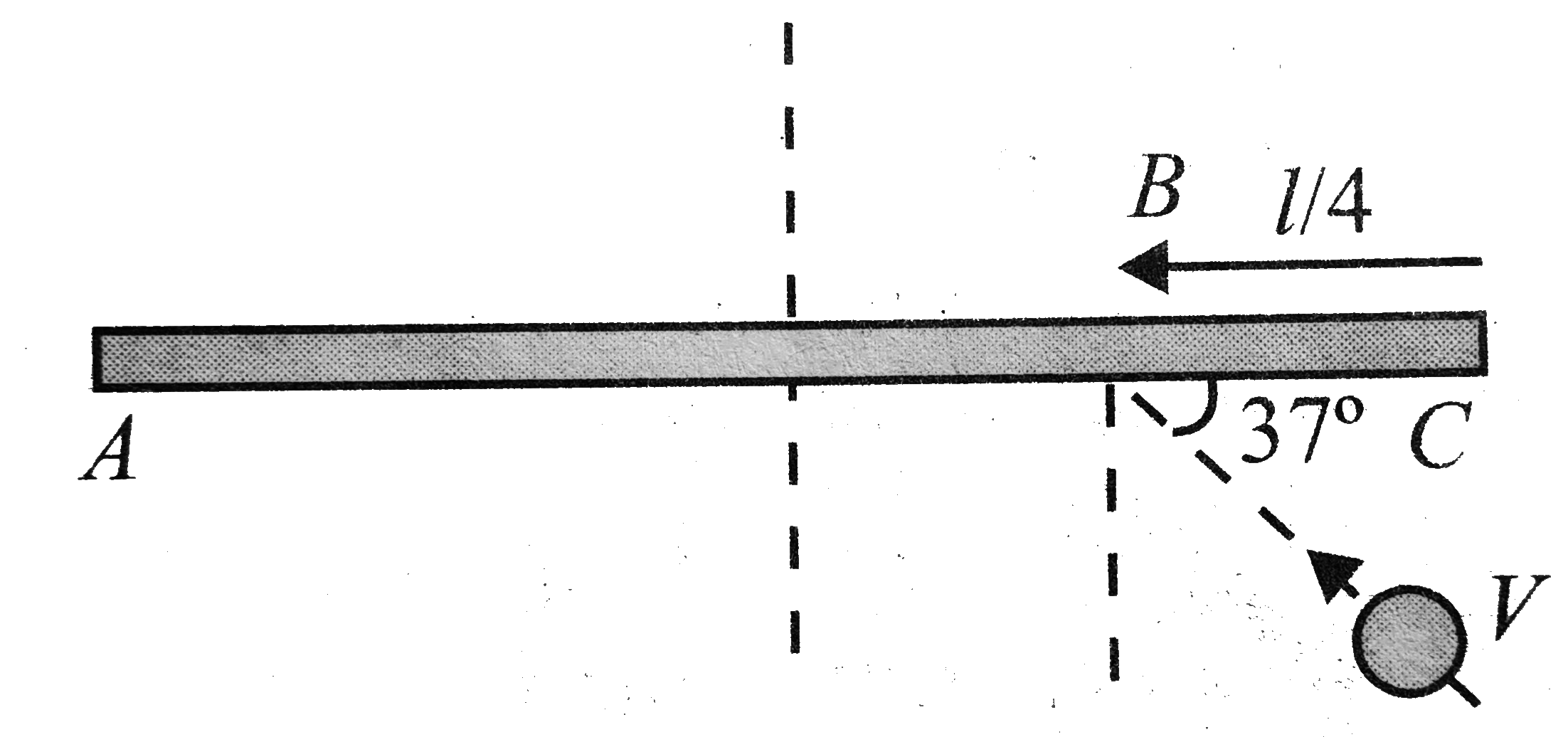
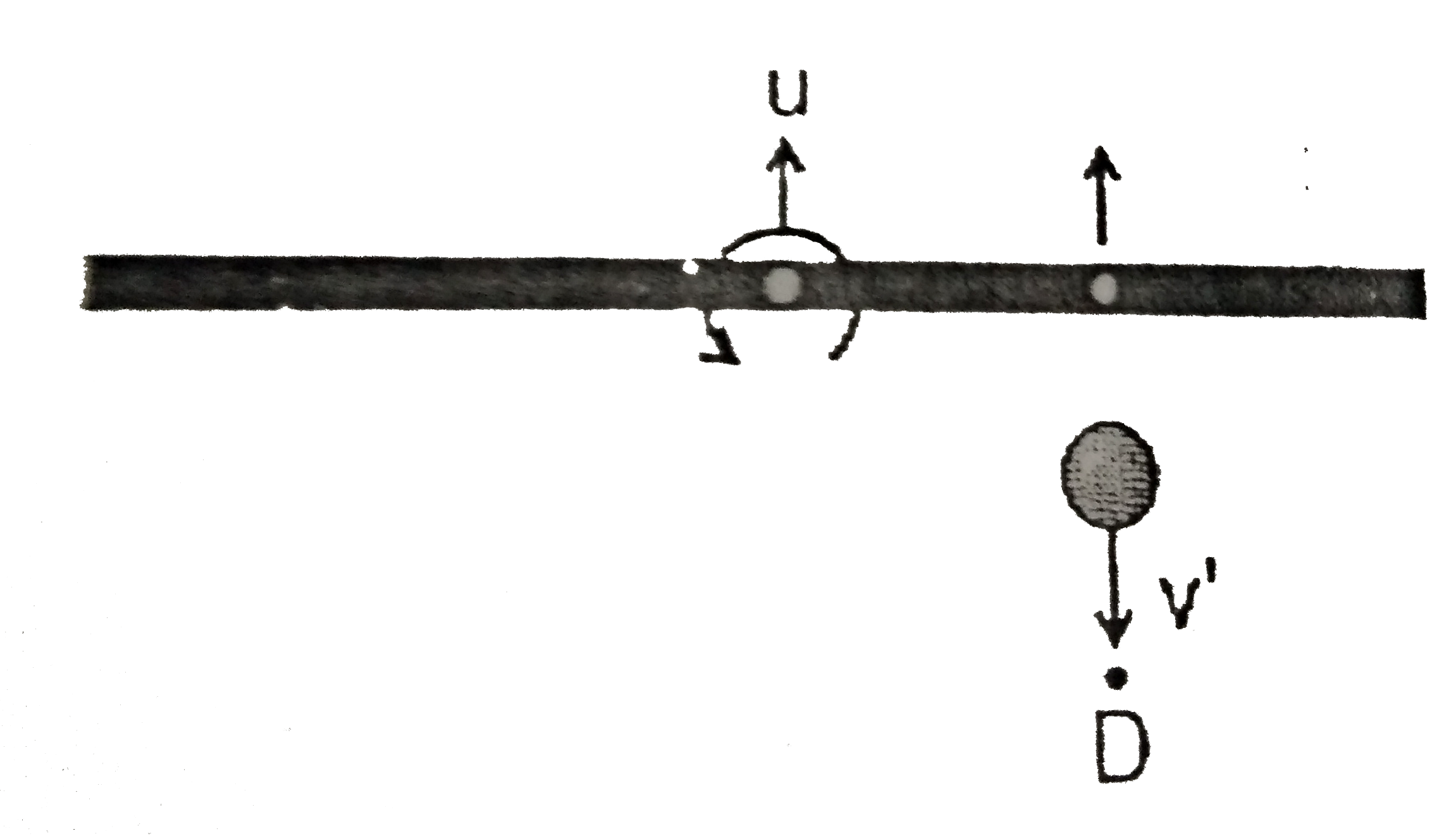
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 69|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 70|7 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 67|2 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|54 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp 68
- A body of mass m is released from a height h on a smooth inclined plan...
Text Solution
|
- A man pulls a solid cylinder ( initially at rest ) horizontal by a mas...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform flag pole of length L and mass M in pivoted on the ground wi...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A (5 kg) and B( 5kg) attached to the ends of a spring const...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AC of length l and mass m is kept on a horizontal smooth plane. ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of dimensions axxaxx2a is kept on an inclined plane of inclina...
Text Solution
|
- Two separate cylinders of masses m(=1 kg ) & 4m radii R(=10cm) and 2R ...
Text Solution
|