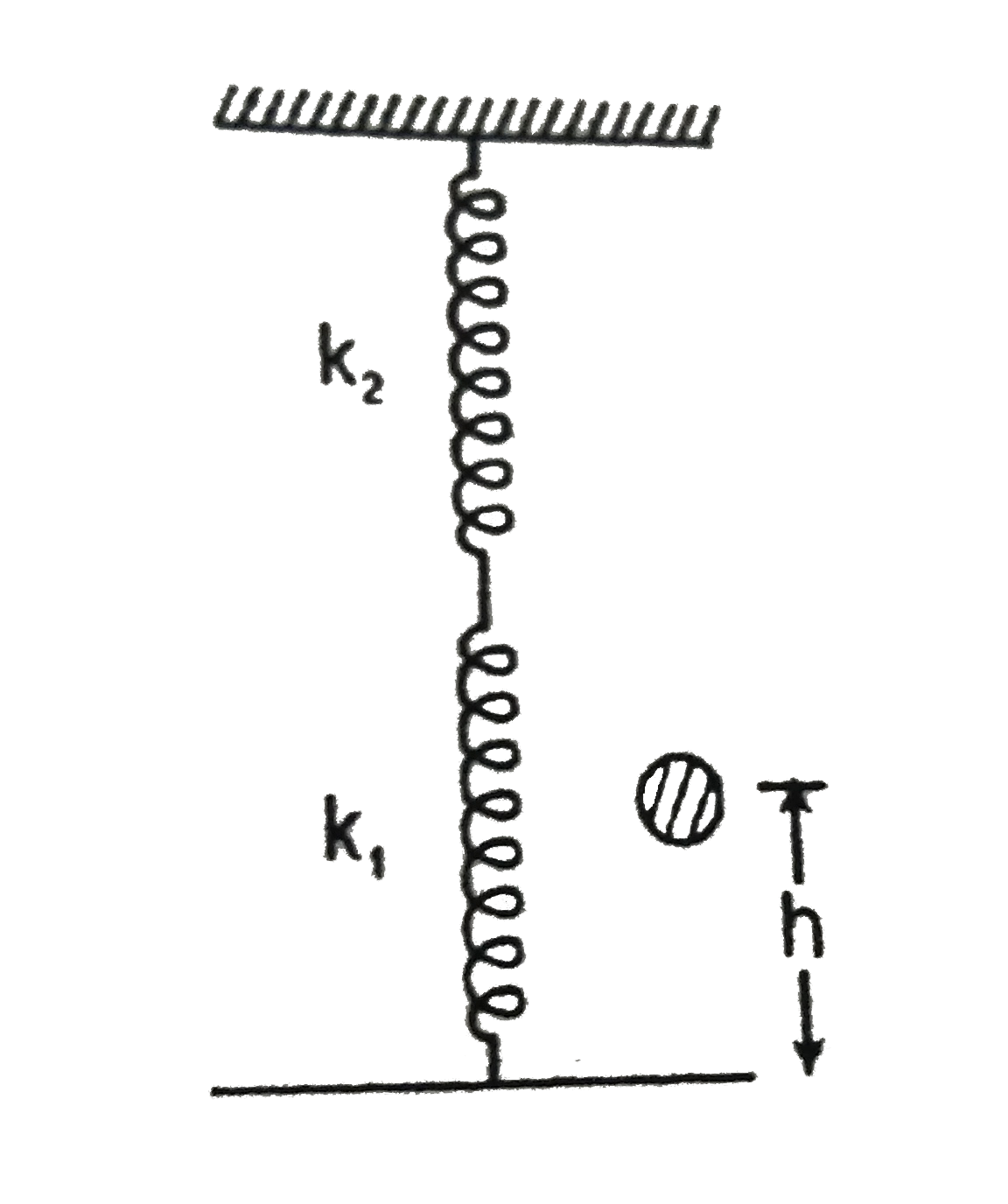
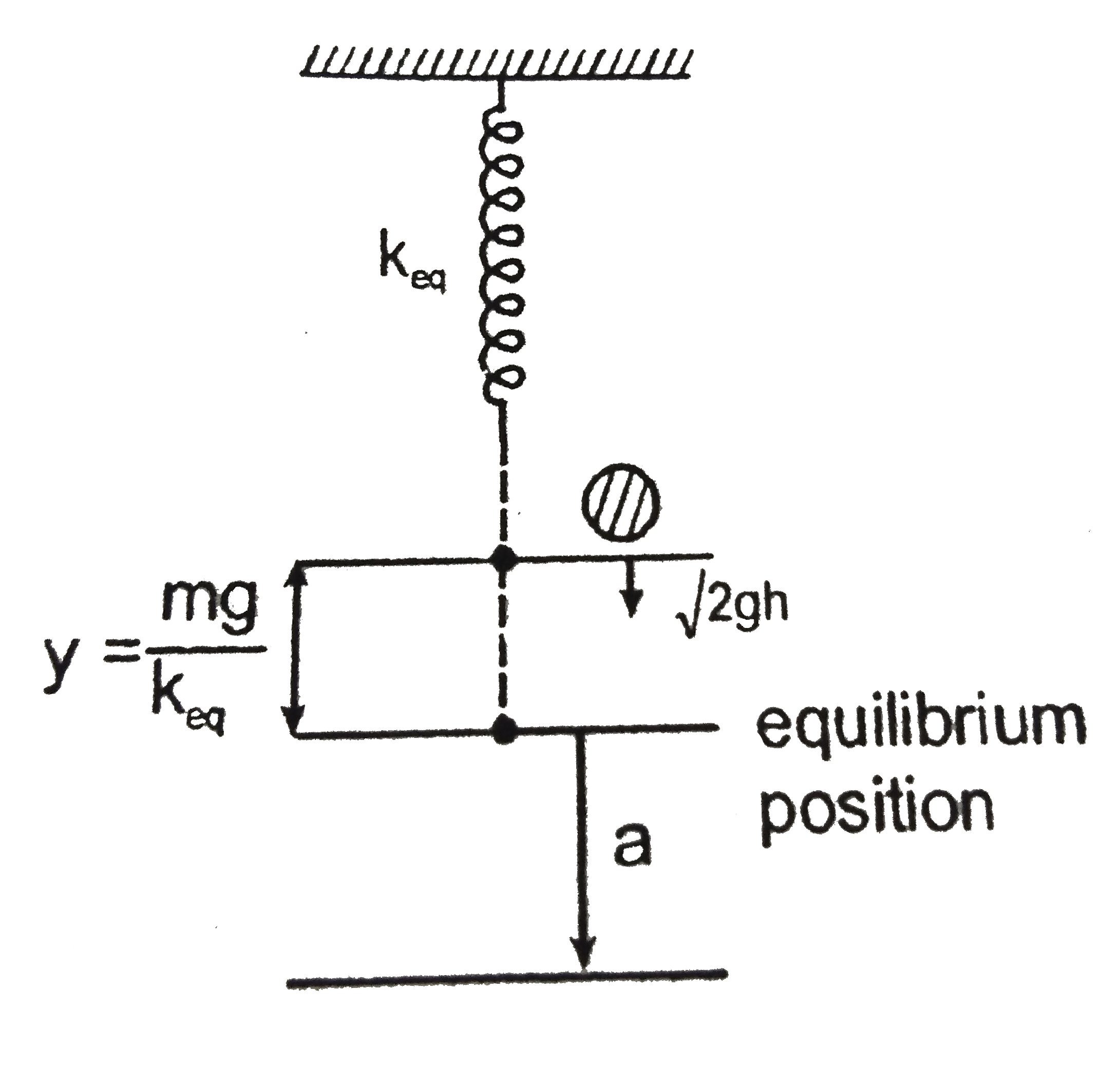
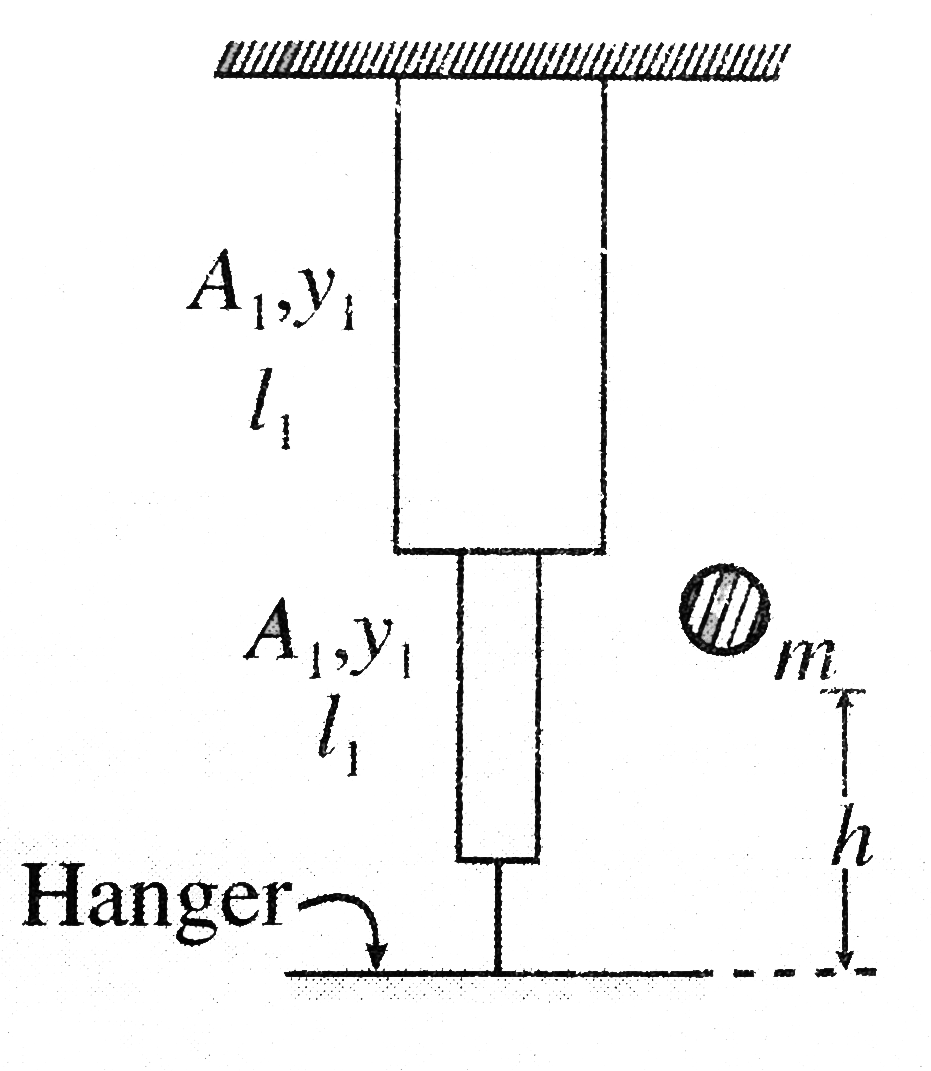Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 91 illustration|2 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 92 illustration|2 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 89 illustration|5 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|54 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems