A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-ELECTROSTATICS-Exercise
- If the electric flux entering and leaving an enclosed surface respecti...
Text Solution
|
- The number of electrons to be put on a spherical conductor of radius 0...
Text Solution
|
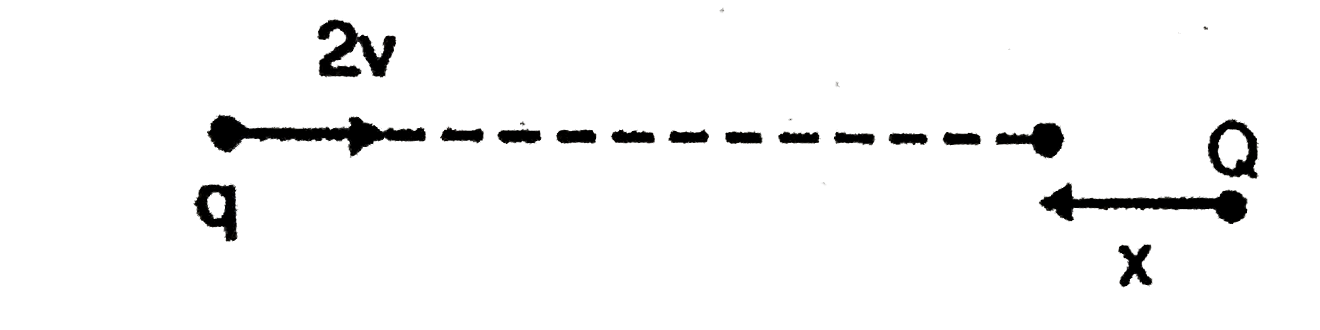
- A charge particle 'q' is shot towards another charged particle 'Q' whi...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge +Q is placed at the centroid of an equilateral triangle...
Text Solution
|
- Four positive charges (2sqrt2-1)Q are arranged at the four corners of ...
Text Solution
|
- Point charges +4q, -q are kept on the x-axis at points x=0,x=a and X=2...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of mass m and charge +q is suspended vertically by a...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows the arrangement of three small uniformally charged s...
Text Solution
|
- Figure, shown above, shows three situations involving a charged partic...
Text Solution
|
- There are three concentric thin spheres of radius a,b,c (agtbgtc). The...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge -q and mass m moves in a circle of radius r aroun...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shown represents the electric field between two large metal...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of electric field on the y-axis as a function of 'y' is ...
Text Solution
|
- A ring carries a uniform linear charge density on one half and the lin...
Text Solution
|
- Two very large thin conducting plates having same cross sectional are...
Text Solution
|
- Two semicircular rings lying in same plane, of uniform linear charge d...
Text Solution
|
- A non-uniformly charged ring is kept near an uncharged conducting soli...
Text Solution
|
- A mercury drop of water has potential 'V' on its surface. 1000 such dr...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge of 5C is placed at point P (as shown in figure). A unit...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is revolving around a proton. The total work done in one r...
Text Solution
|