A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-PART TEST 1-Exercise
- A soldi sphere a hollow sphere and a disc, all haing same mass and rad...
Text Solution
|
- Statement 1: A solid sphere and a hollow sphere of same radius and sam...
Text Solution
|
- A 1 kg block is being pushed against a wall by a force F=75N as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A force vec F = (3t hat i + 5 hat j)N acts on a body due to which its ...
Text Solution
|
- Particle 'A' moves with speed 10m//s in a frictionless circular fixed ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic wire of diameter d is lying horizontally o the surface of w...
Text Solution
|
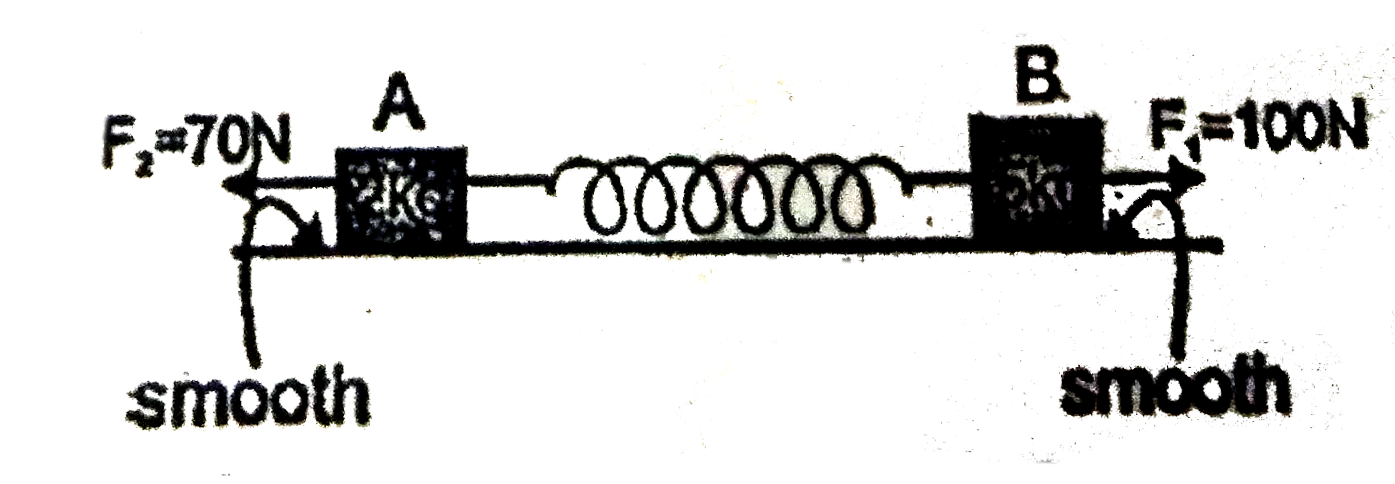
- Two constant horizontal force F1 and F2 are acting on blocks A and B. ...
Text Solution
|
- If the energy ( E) ,velocity (v) and force (F) be taken as fundamental...
Text Solution
|
- Statement 1: Two spheres undergo a perfectly elastic collision. The ki...
Text Solution
|
- A shere of mass m , moving with velocity V, enters a hanging bag of sa...
Text Solution
|
- Each point mass 2 kg is connected at the end of each uniform rod of le...
Text Solution
|
- Reading of spring balance S1 and S2 (Pulley are ideal)
Text Solution
|
- A wheel of radius 0.4m can rotate freely about its axis as shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball of mass 1kg strikes a wedge of mass 4kg horizontally with...
Text Solution
|
- A lift is moving in upward direction with speed 20m//s and having acce...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is released from a height h on a smooth inclined plan...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is fastened to a string. The ball swings in a vertica...
Text Solution
|
- If y=x-x^2 is the path of a projectile, then which of following is inc...
Text Solution
|
- Value of theta is increased gradually from theta = 0. At theta = tan^(...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure (i) half of the meter scale is made of wood while the ot...
Text Solution
|