A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-PART TEST 5-Exercise
- Figure shows a solid hemisphere with a charge of 5 nC distributed unif...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two concentric shells of radii a and b uniformly distribu...
Text Solution
|
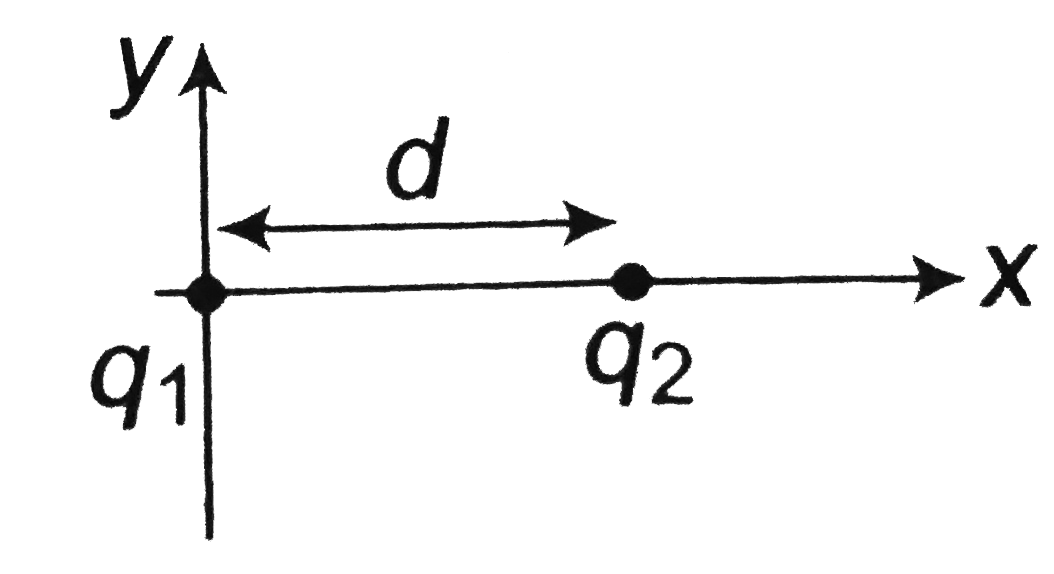
- Two particles of charge q(1) and q(2) are separated by distance d as s...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed ring of radius R is given a charge q. A charge q0 is brought s...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure two concentric conducting shells of radius R & 2R are sh...
Text Solution
|
- Two equipotential spherical surface having potential 20V and 0V are as...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity at all points in space is given by vecE =...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric conducting thin shells of radius R and 2 R carry charge...
Text Solution
|
- A uniformly charged non-conducting spherical shell is given +q charge ...
Text Solution
|
- Find out the potential of the junction S (in volts) if all the dark wi...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown R = 100 Omega L = (2)/(pi) H and C = (8)/(pi) mu F...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform field is exists in the region directed away from the page. A...
Text Solution
|
- When the number of turns in a coil is doubled without any change in th...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference across 8 ohm resistance is 48 volt as shownin...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit, in steady state we may say: (capacitors are init...
Text Solution
|
- Two circular rings of identical radii and resistance of 36Omega each a...
Text Solution
|
- At distance 'r' from a point charge, the ratio (U)/(V^(2)) (where 'U' ...
Text Solution
|
- A graph between current and time during charging of a capacitor by a b...
Text Solution
|
- An electron passes between two parallel plate of a capacitor as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- Three distinct current carrying wires intersect a finite rectangular p...
Text Solution
|