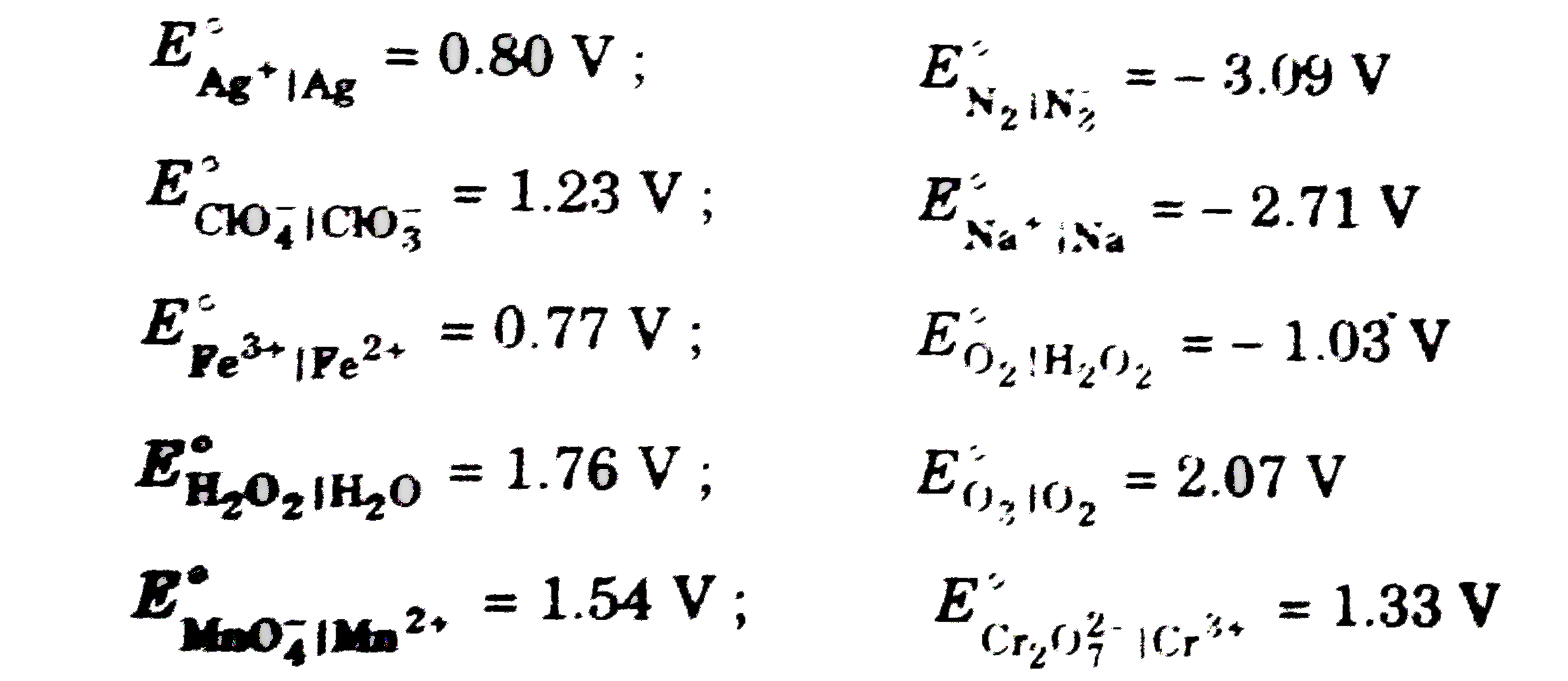A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Standard reduction potentials (SRP) for different systems can be used ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the oxidant and the reductant in the following reactions: a...
Text Solution
|
- Reduction potential for the following h alf-cell reaction are Zn rarr ...
Text Solution
|
- Standard reduction electrode potential of Zn^(2+)//Zn is -0.76V. This ...
Text Solution
|
- Standard reduction potentials (SRP) for different systems can be used ...
Text Solution
|
- Standard reduction potentials (SRP) for different systems can be used ...
Text Solution
|
- Standard reduction potentials (SRP) for different systems can be used ...
Text Solution
|
- STATEMENT-1: If SRP of substance is -0.5V, then reduction of substance...
Text Solution
|
- The standard reduction potential of Zn-electrode is -0.76V. The standa...
Text Solution
|