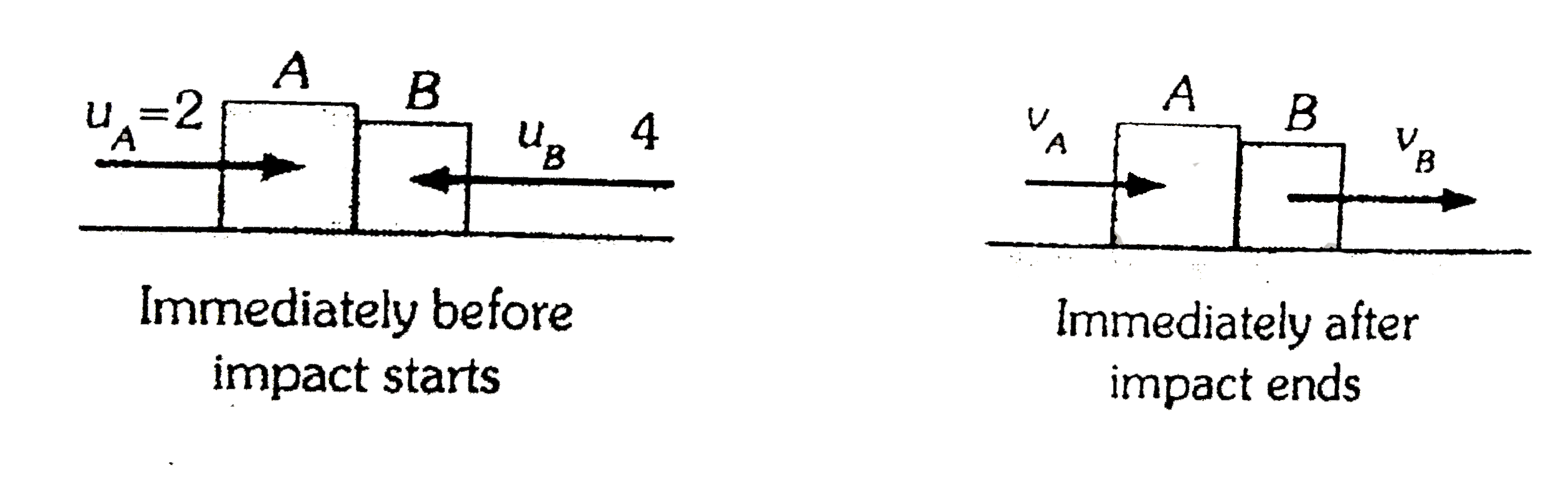Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-I|40 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-II|43 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-IV ASSERTION & REASON|11 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise 5 B (Integer Type Questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-CENTRE OF MASS-EXERCISE-V B
- A block of mass 5 kg moves from left to right with a velocity of 2ms^(...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m(1) and m(2) in projectile motion have veloci...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negli...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in the X-Y plane under the influence of a force such ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small particles of equal masses stant moving in opposite directio...
Text Solution
|
- Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is projected from the ground with an initial spee...
Text Solution
|
- A tennis ball dropped on a barizoontal smooth surface , it because bac...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls , having linear momenta vec(p)(1) = p hat(i) and vec(p)(2) =...
Text Solution
|
- STATEMENT-l : In an elastic collision between two bodies, the relative...
Text Solution
|
- Satement-1: if there is no external torque on a body about its centre ...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M move on a frictionless surface of an inclimed...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M move on a frictionless surface of an inclimed...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M move on a frictionless surface of an inclimed...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 2kg and M are at rest on an inclined plane and ar...
Text Solution
|
- A car P is moving with a uniform speed 5sqrt3 m//s towards a carriage ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m, moving in a cicular path of radius R with a cons...
Text Solution
|
- Two point masses m1 and m2 are connected by a spring of natural length...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular plate of mass M and dimension axxb is held in horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- Three objects A , B and C are kept in a straight line on a smooth hori...
Text Solution
|