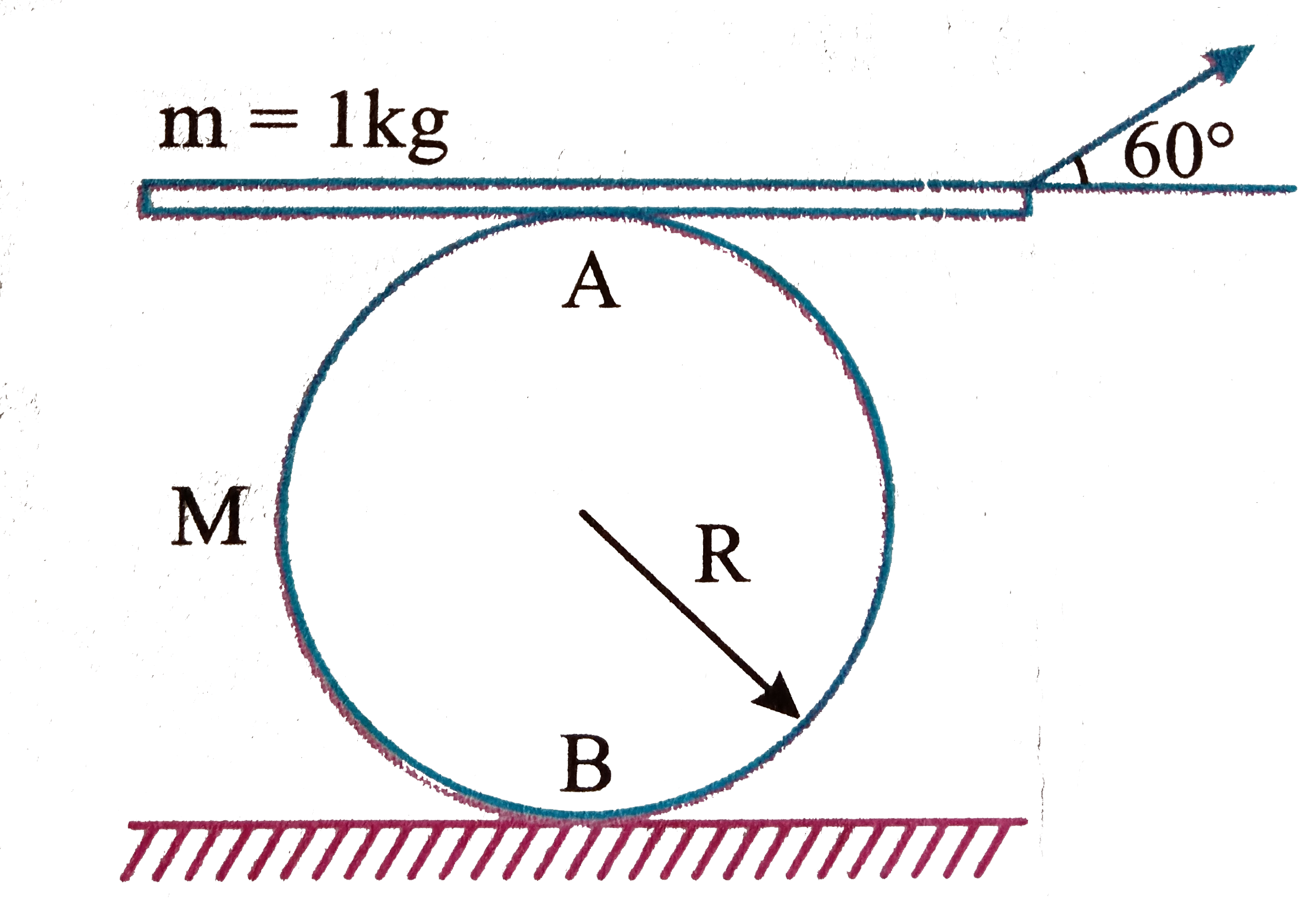A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DISHA-ROTATIONAL MOTION-physics
- A child is standing with folded hands at the center of a platform rota...
Text Solution
|
- Two uniforms discs of equal mass but unequal radii are mounted on fixe...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cylinder of mass M=1 kg and radius R=1 mlying on a rough ho...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cylinder of mass M=1 kg and radius R=1 mlying on a rough ho...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cylinder of mass M=1 kg and radius R=1 mlying on a rough ho...
Text Solution
|
- Statement -1 : Torque is equal to rate of change of angular momentum ....
Text Solution
|
- Statement -1: Torque due to force is maximum when angle between vec r ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement -1: It is harder to open and shut the door if we apply force...
Text Solution
|
- Five particles of mass 2 kg are attached to the rim of a circular disc...
Text Solution
|
- Two discs of the same material and thickness have radii 0.2 m and 0.6 ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of 500 g and radius 10 cm has moment of inertia (about its ...
Text Solution
|
- A constant torque of 31.4 N-m id exterted on a pivoted wheel. If the a...
Text Solution
|
- From a uniform wire, two circular loops are made (i) P of radius r and...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a sphere of mass M and radius R about an axis...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles each of mass m are placed at the corners of a square of...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of gyration of a disc of mass 50 g and radius 2.5 cm, about...
Text Solution
|
- Moment of inertia of a ring of mass m = 3 gm and radius r = 1 cm about...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is of mass M and radius r. The moment of inertia of it about an...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres each of mass M and radius R//2 are connected at their cent...
Text Solution
|
- Three point masses m(1), m(2) and m(3) are located at the vertices of ...
Text Solution
|