A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DISHA-RAY OPTICS-physics
- Light of wavelength 6000Å enters from air into water (a medium of refr...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light falls on a glass plate of refractive index mu=1.5. ...
Text Solution
|
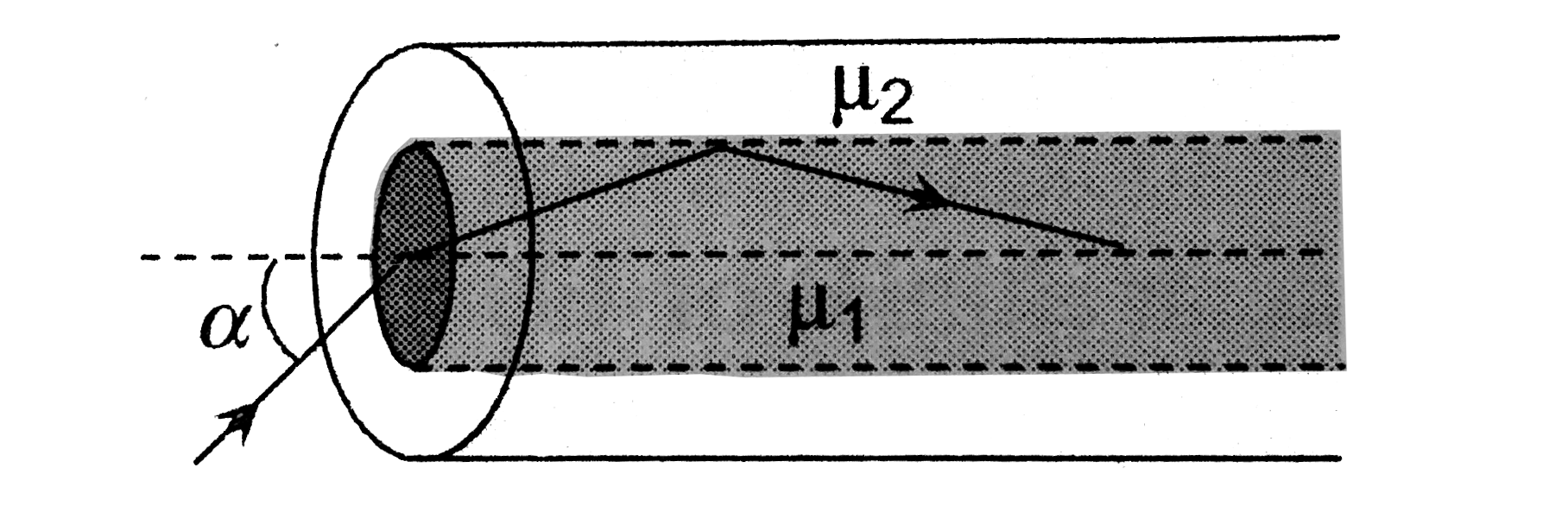
- An optical fibre consists of core of mu(1) surrounded by a cladding of...
Text Solution
|
- A glass plate 4 mm thick is viewed from the above through a microscope...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical microscope is focussed on a point at the bottom of an empty...
Text Solution
|
- Light from a sodium lamp (lambda0=589 nm) passes through a tank of gly...
Text Solution
|
- A light beam is traveling from Region I to region IV (refer figure). T...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive index of the material of a prism is sqrt(2) and its pri...
Text Solution
|
- When light rays are incident on a prism at an angle of 45^(@), the min...
Text Solution
|
- A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 and angle of prism 6^(@) is put ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the dispersive power for crown glass from the given data m...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the angle of a prism of dispersive power 0.021 and refractiv...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light falls on a normally on a refracting face of a prism. Fi...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive indices of material of a prism for blue and red colours...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from a height of 20 m above the surface of water in ...
Text Solution
|
- A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water (refractive...
Text Solution
|
- A prism having an apex angle of 4^@ and refractive index of 1.50 is lo...
Text Solution
|
- Let the x-z plane be the boundary between two transparent media. Mediu...
Text Solution
|
- Dispersive power does not depend upon
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : There is no dispersion of light refracted through a rectan...
Text Solution
|