A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Velocity at a general point P(x, y) for a horizontal projectile motion...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of motion of a projectile is y = 12 x - (3)/(4) x^2. The ...
Text Solution
|
- In fig., blocks A and B move with velocities v(1) and v(2) along horiz...
Text Solution
|
- In a projectile motion let v(x) and v(y) are the horizontal and vertic...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity at a general point P(x, y) for a horizontal projectile motion...
Text Solution
|
- elocity at a general point P(x, y) for a horizontal projectile motion ...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity at a general point P(x, y) for a horizontal projectile motion...
Text Solution
|
- Letvec(V) =v(x)hat(i)+v(y)hat(j)+v(z)hat(k), then int(t(1))^(t(2)) V(y...
Text Solution
|
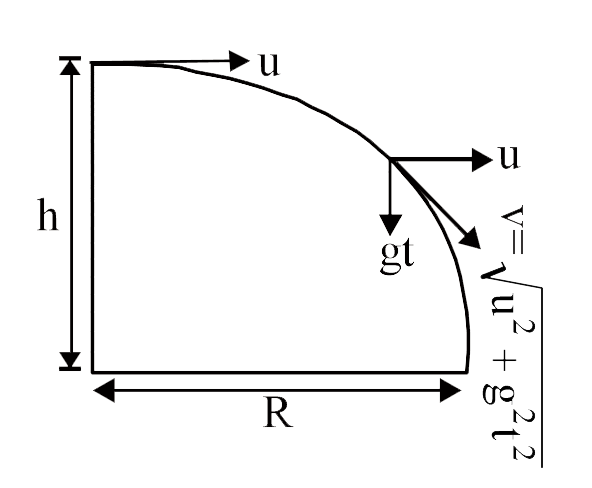
- A projectile is thrown horizontally forma height 'h' a shown in the fi...
Text Solution
|