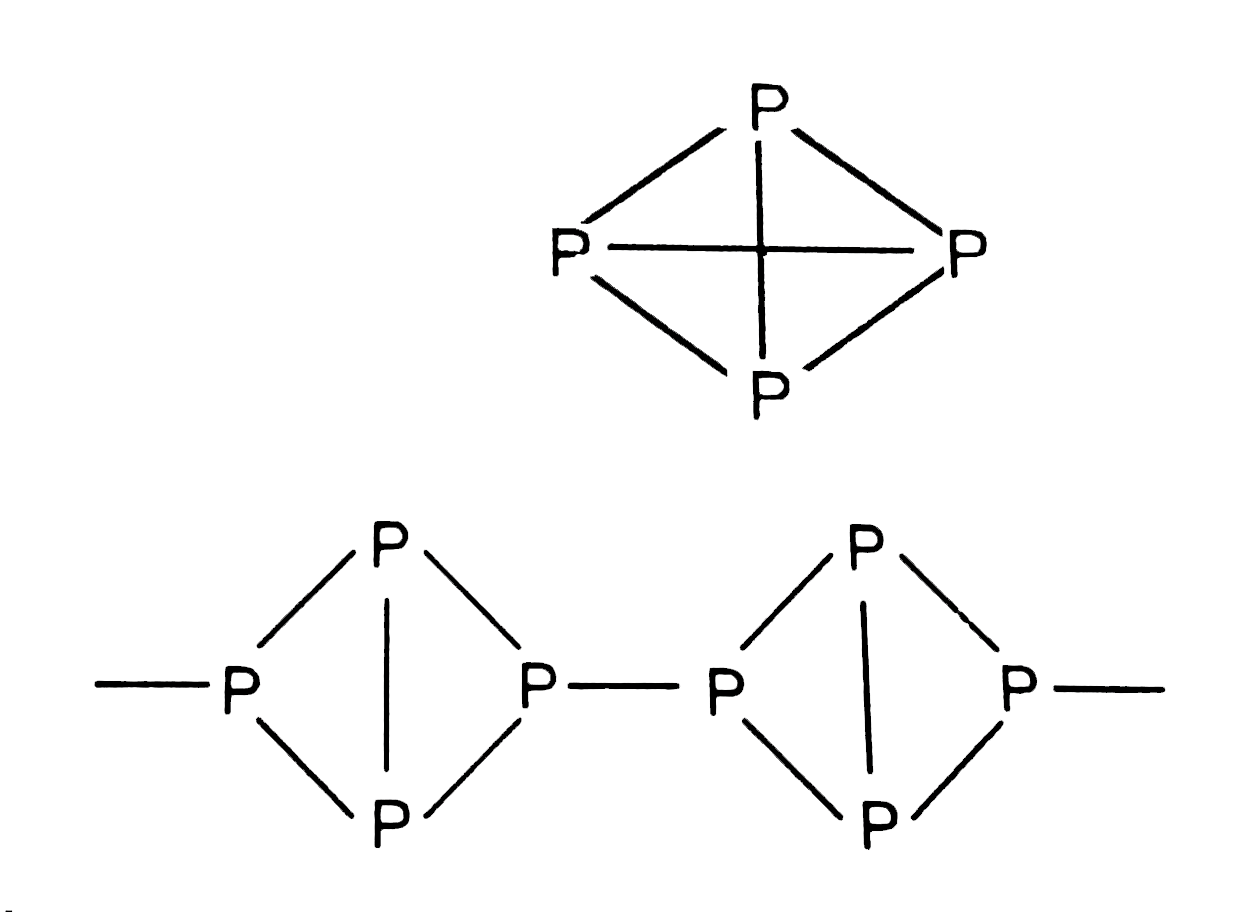
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
P BLOCK ELEMENTS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise 1 part-1|14 VideosP BLOCK ELEMENTS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise 1 part-2|32 VideosP BLOCK ELEMENTS
RESONANCE|Exercise ALP PART OBJECTIVE|12 VideosNUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
RESONANCE|Exercise STAGE-II|1 VideosP-BLOCK ELEMENT (BORON AND CARBON FAMILY)
RESONANCE|Exercise PART - III : OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS (PREVIOUS YEARS) STAGE - V (INTERNATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD (IChO)) Problem 3|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-P BLOCK ELEMENTS-B.L.E
- Why is H(2)O a liquid and H(2)S a gas?
Text Solution
|
- The stability of +5 oxidation state decreases down the group 15 of the...
Text Solution
|
- (a)What happens when white phosphorus is heated with concentrated NaOH...
Text Solution
|
- What are the oxidation states of phosphorus in the following: (i)H(3...
Text Solution
|
- (a)Give reasons for the following : Nitric oxide becomes brown when re...
Text Solution
|
- Why is ICI more reactive than I2?
Text Solution
|
- Why is helium used in diving apparatus ?
Text Solution
|
- With which neutral molecule is ClO^(-) isoelectronic ? Is this molecul...
Text Solution
|
- Why has it been difficult to study the chemistry of radon ?
Text Solution
|
- How are XeO(3) and XeOF(4) prepared ?
Text Solution
|
- List the uses of neon and argon gases.
Text Solution
|
- Explain why fluorine forms only one oxoacid, HOF.
Text Solution
|
- Explain why inspite of nearly the same electronegativity, nitrogen for...
Text Solution
|
- Write two uses of ClO2.
Text Solution
|
- Why are halogens coloured?
Text Solution
|
- How can you prepare Cl2 from HCl and HCI from Cl2? Write reactions onl...
Text Solution
|
- How are xenon fluorides XeF(2),XeF(4) and XeF(6) obtained?
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following does not exist ? (i) XeOF(4) (ii) NeF(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- Why do noble gases have comparatively large atomic sizes?
Text Solution
|
- Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electro...
Text Solution
|