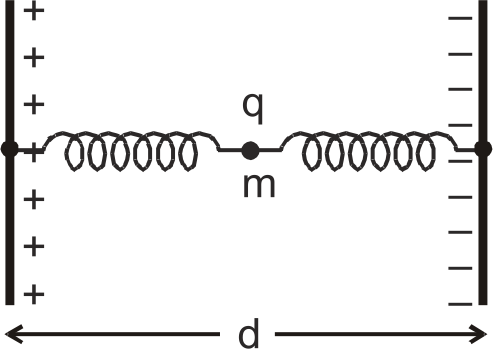
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two large non conducting plates having surface charge densities +sigma...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown A & B are two charged particles having charges q a...
Text Solution
|
- Two large non conducting plates having surface charge densities +sigma...
Text Solution
|
- Plate A of parallel plate air filled capacitor is connected to a sprin...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 5 kg having charge q is attached to a spring of const...
Text Solution
|
- Two non-conducting hemispherical surface, which are having uniform cha...
Text Solution
|
- The plates each of area A of a parallel plate caoacitor are given char...
Text Solution
|
- Two large insulating plates having surface charge densities + sigma an...
Text Solution
|
- Two charged capacitors have their outer plates fixed and inner plates ...
Text Solution
|