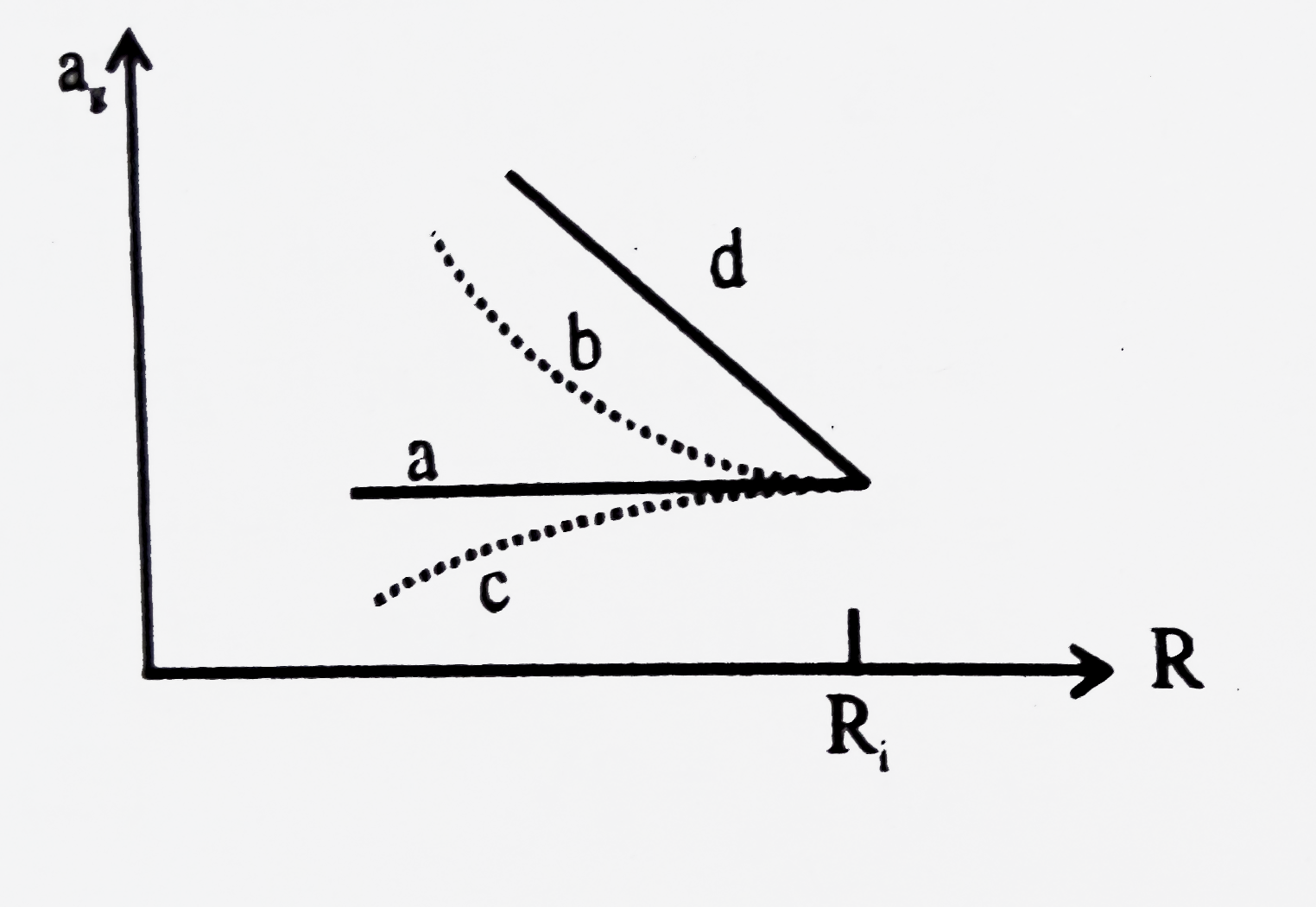
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DISHA-GRAVITATION-Physics
- A body weighs 72 N on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitatio...
Text Solution
|
- A body weighs W newton at the surface of the earth. Its weight at a he...
Text Solution
|
- A shell of mass M and radius R has point mass m placed at a distance r...
Text Solution
|
- The largest and the shortest distance of the earth from the sun are r(...
Text Solution
|
- A planet is moving in an elliptic orbit. If T,V,E and L stand, respect...
Text Solution
|
- The earth is assumed to be a sphere of raduis R. A plateform is arrang...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of mass M and radius R is surrounded by a spherical she...
Text Solution
|
- A body starts from rest from a point distant r(0) from the centre of t...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite of mass M is moving in a circle of radius R under a centri...
Text Solution
|
- The change in the value of g at a height h above the surface of the ea...
Text Solution
|
- Two indentical geostationary satellite each of mass m are moving with ...
Text Solution
|
- A diametrical tunnel is dug across the earth. A ball dropped into the ...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite revolves around the earth of radius R in a circular orbit ...
Text Solution
|
- A(nonrotating) star collaps onto from an initial radius R(i) with its ...
Text Solution
|
- if the earth is treated as a sphere of radius Radn mass M, Its angular...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is launched into a circular orbit of radius R around the e...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform spherical shell gradually shrinks maintainig its shape. The ...
Text Solution
|
- The depth at which the value of acceleration due to gravity is 1/n tim...
Text Solution
|
- Radius of moon is 1//4 times that of earth and mass is 1/81 times that...
Text Solution
|
- What is the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass m fr...
Text Solution
|