A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DISHA-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-PHYSICS
- Calculate the rms speed of smoke particles of mass 5 xx 10^(-17) kg i...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas requires 207J heat to raise the temperature b...
Text Solution
|
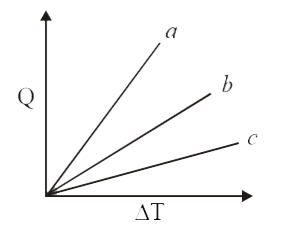
- Figure shows the variation in temperature (DT) with the amount of heat...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mole of a monatomic and 2 mole of a diatomic gas are mixed. The resu...
Text Solution
|
- The density of a gas is 6xx 10^(-2 )kg//m^(3) and the root mean square...
Text Solution
|
- The absolute temperature of the gas is increased 3 times. What will be...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an ideal gas confined in an isolated closed chamber. As the g...
Text Solution
|
- One kg of a diatomic gas is at pressure of 8xx10^4N//m^2. The density ...
Text Solution
|
- A thermally insulated vessel contains an ideal gas of molecular mass M...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a parabolic graph between T and 1/V for a mixture of a ga...
Text Solution
|
- The work of 146 kJ is performed in order to compress one kilo mole of ...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperature is the root mean square velocity of gaseous hydrog...
Text Solution
|
- The kinetic theory of gases states that the average squared velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- If 2 mol of an ideal monatomic gas at temperature T(0) are mixed with ...
Text Solution
|
- From the following statements concerning ideal gas at any given temper...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the pressure P versus volume V graphs for a certains mass...
Text Solution
|
- The molecules of a given mass of a gas have rms velocity of 200 m//s a...
Text Solution
|
- A graph is plotted with PV/T on y-axis and mass of the gas along x-axi...
Text Solution
|
- At identical temperatures, the rms speed of hydrogen molecules is 4 ti...
Text Solution
|
- Find the expression for the work done by a system undergoing isotherma...
Text Solution
|