A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-TEST PAPERS-MATHEMATICS
- If int(-20)^(-10)((x^(2)-x)/(x^(3)-3x+1))^(2)+dx+int(1/21)^(1/11)((x^(...
Text Solution
|
- Solution of the differential equation x^(2)dy-2xydx=x^(3)y^(3)dx+x^(4)...
Text Solution
|
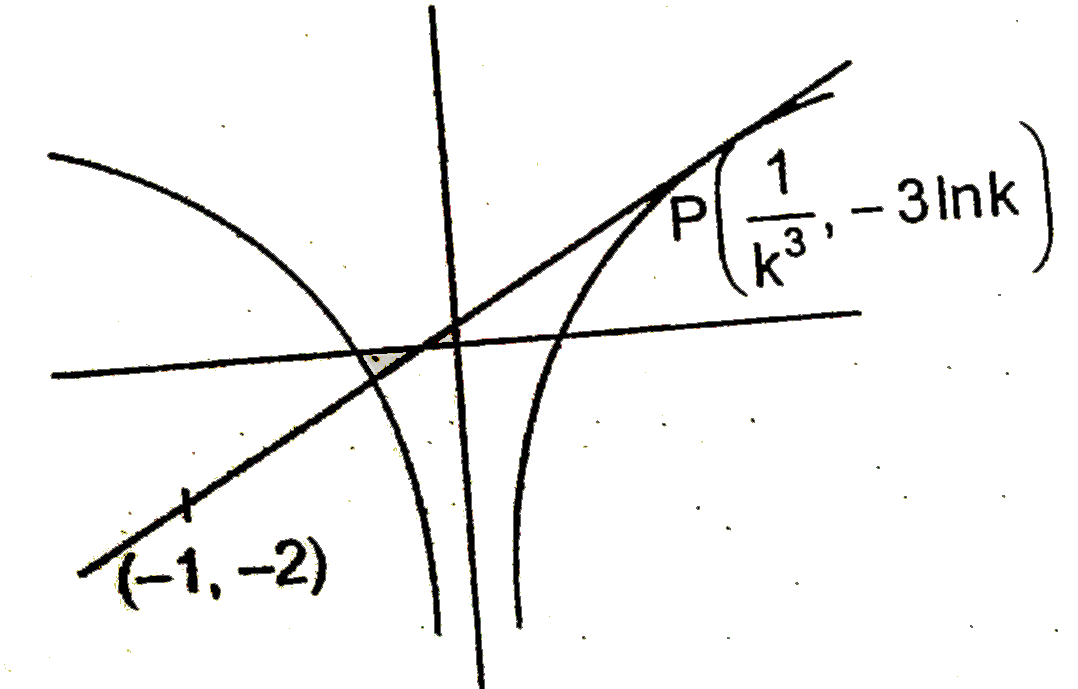
- If f(x)=k^(3)x+k^(3)-2 cuts the curve g(x)=1/2Inx^(2) at exactly one p...
Text Solution
|
- Let =f(x) be the solution of the diferential equation y^(')=(3y^(2)+x)...
Text Solution
|
- The solution of the differential equation (x^(2)+4y^(2)-5)xd=(4x^(2)-3...
Text Solution
|
- Let functions are defined from set A to set B where B={alpha,beta} and...
Text Solution
|
- If f(x) is a twice differentiable function and given that f(1)=2,f(2)=...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)={(0 , x "is irrational"),(2/(2q^(3)-q^(2)+q+sin^(2)q+5) , if ...
Text Solution
|
- Let y=f(x) be the solution of the differential equation (dy)/(dx)+k/7 ...
Text Solution
|
- Let y=f(x) be the solution of the differential equation (dy)/(dx)+k/7 ...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)={(|x-1|+|x-2|, ,, 2ge1),(x, ,, xlt1):} and g(x)={("max"{f(t):...
Text Solution
|
- Let Q(x) be a function defined for xepsilon [e^(3), e^(6)] be a real v...
Text Solution
|
- If lim(xtoI^(-)) prod(n=0)^(oo)((1+x^(n+1))/(1+x^(n))^(x^n))=l then [1...
Text Solution
|
- If the least bounded by the curves y=x^(2) and y=lamdax+12 is equal to...
Text Solution
|
- The range of real constant t for which (1-tan^2 t)sin theta^2+tan^2 t...
Text Solution
|
- The complete set of non-zero values of 'k' such that the equation |x^(...
Text Solution
|
- Let f be the real valued differentiable function on R such that e^(-x)...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)=[x]+{x}^(3) then the area of the figure bounded by y=f^(-1)(x...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of distinct x epsilon [0,1] for which int(0)^(x) (t^(8)+1...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)=ax^(17)+bsinx.sin2x.sin3x+cx^(2) sgn(sin x)+d log (x+sqrt(1+x...
Text Solution
|