A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-TEST PAPERS-MATHEMATICS
- x(1), x(2), x(3) are three real numbers satisfying the system of equat...
Text Solution
|
- a(1), a(2), a(3),…………. are distinct terms of an A.P. We cal (p,q,r) an...
Text Solution
|
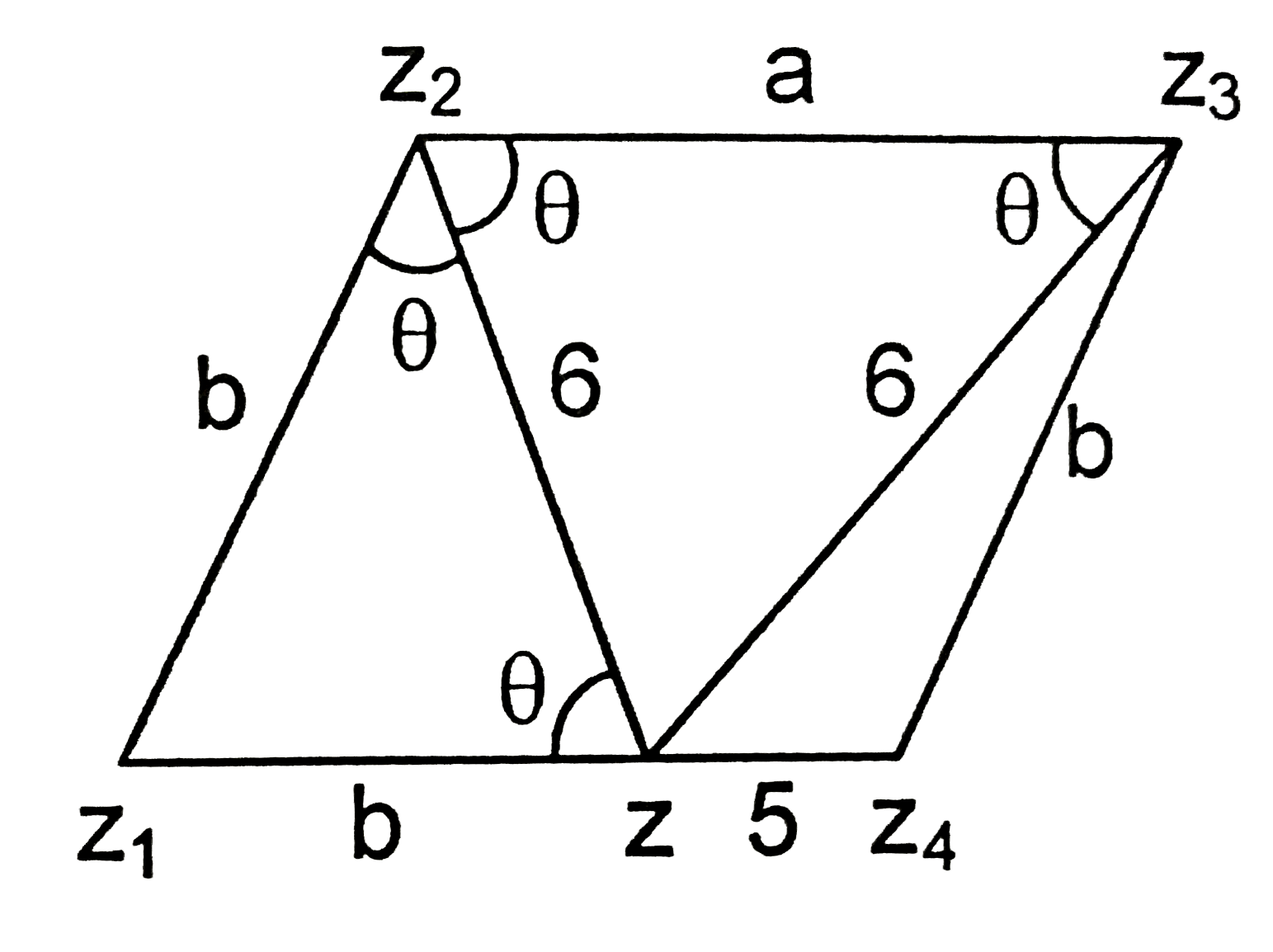
- If z(1), z(2), z(3), z(4) are complex numbers in an Argand plane satis...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is/are true?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is/are correct?
Text Solution
|
- The vertices of a triangle ABC are A-=(2,0,2), B(-1,1,1) and C-=(1,-2,...
Text Solution
|
- Find the direction cosines of the lines, connected by the relations...
Text Solution
|
- Let the equation of a straight line L in complex form be abarz+baraz+b...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Column I- with Column-II
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Column I- with Column-II
Text Solution
|
- If alpha(1),alpha(2),alpha(3), alpha(4) are the roos of x^(4)+2x^(3)+b...
Text Solution
|
- A chess match between two players A and B is won by whoever first wins...
Text Solution
|
- If k(1) and k(2) (k(1) gt k(2)) are two non-zero integral values of k ...
Text Solution
|
- Let ak = .^nCk for 0 lt= k lt= n and Ak = [(a(k-1),0), (0,ak)] for 1 l...
Text Solution
|
- If sum(r=0)^(203)((r^(2)+2)(r+1)!+2r(r+1)!)=a!-2(b) (where a,b in N), ...
Text Solution
|
- If a=1+x^3/(3!)+x^6/(6!)+.....oo, b=x+x^4/(4!)+x^7/(7!)+.....oo , c=...
Text Solution
|
- Let A=[(l,m,n),(p,q,r),(1,1,1)] and B=A^(2). If (l-m)^(2)+(p-q)^(2)=9,...
Text Solution
|
- If the number of ordered pairs (a,b) where a,b in R such that (a+ib)^(...
Text Solution
|
- A is a matrix of 3xx3 and a(ij) is its elements of i^(th) row and j^(t...
Text Solution
|
- If x and y satisfy te equation xy-2x^(2)-9x+3y-16=0 then
Text Solution
|