A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-TEST PAPERS-MATHEMATICS
- A is a matrix of 3xx3 and a(ij) is its elements of i^(th) row and j^(t...
Text Solution
|
- If x and y satisfy te equation xy-2x^(2)-9x+3y-16=0 then
Text Solution
|
- Let p, q be integers and let alpha,beta be the roots of the equation ...
Text Solution
|
- For any two positive integers x and y f(x,y)=1/((x+1)!)+1/((x+2)!)+1/(...
Text Solution
|
- Let agt0, bgt0, cgt0 and a+b+c=6 then ((ab+1)^(2))/(b^(2))+((bc+1)^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- A and B play a game in which they alternately call out positive intege...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is/are correct?
Text Solution
|
- Consider all 10 digit numbers formed by using all the digits 0, 1, 2, ...
Text Solution
|
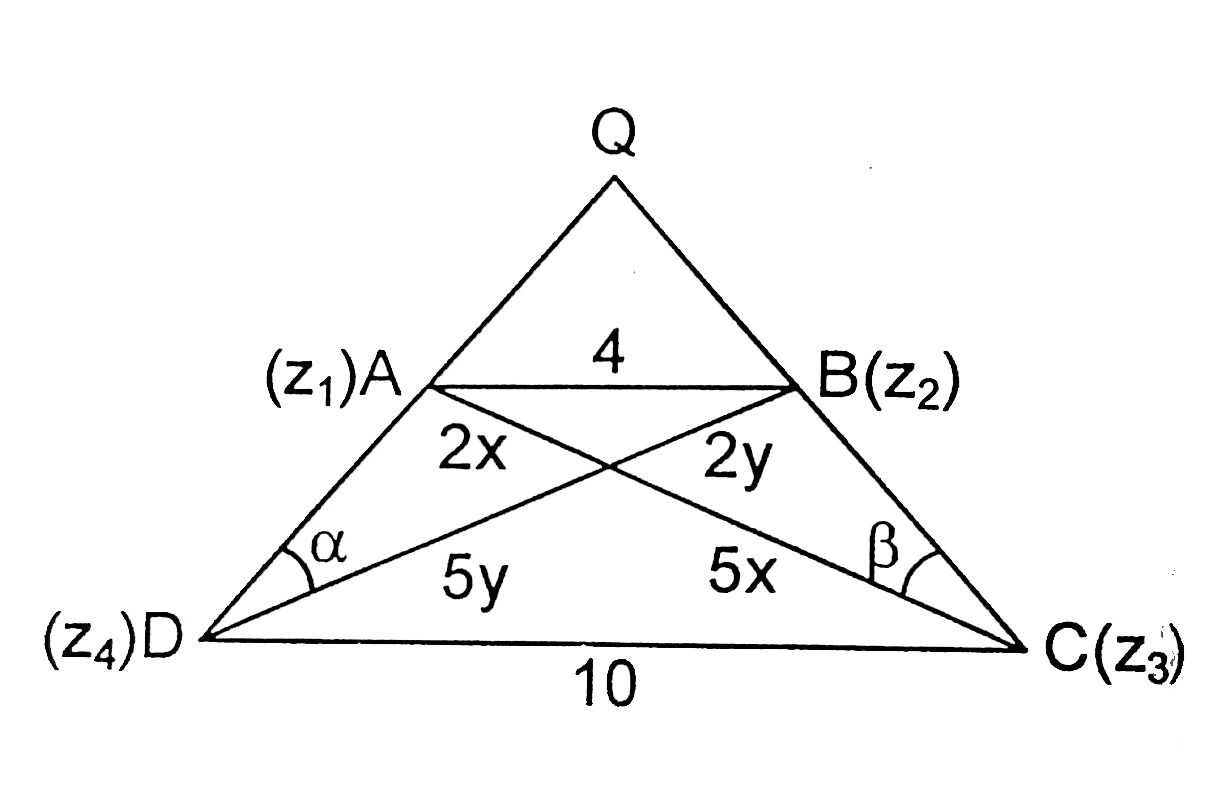
- Let A(z(1)), B(z(2)), C(z(3) and D(z(4)) be the vertices of a trepeziu...
Text Solution
|
- Let A(z(1)), B(z(2)), C(z(3) and D(z(4)) be the vertices of a trepeziu...
Text Solution
|
- In the equation A+B+C+D+E=FG. Where FG is the two digit number whose v...
Text Solution
|
- In the equation A+B+C+D+E=FG. Where FG is the two digit number whose v...
Text Solution
|
- If a,b,c are three positive real numbers then the minimum value of (a+...
Text Solution
|
- If the quadratic equation a(1)x^(2)-a-(2)x+a(3)=0 where a(1),a(2),a(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Let a(1),a(2),a(3),a(4),a(5) be a five term geometric sequence satisfi...
Text Solution
|
- If the coefficient of x^((n^(2)+n-18)/2) in (x-1)(x^(2)-2)(x^(3)-3)(x^...
Text Solution
|
- If a,b,c are three positive numbers then the minimum value of (a^(4)+b...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha^(k) when k=0, 1, 2, 3, 4….253 are 254^(th) roots of unity th...
Text Solution
|
- Let A=[a(ij)](3xx3) be a matrix such that A.A^(T)=4I and a(ij)+2c(ij)=...
Text Solution
|
- If x^(3)+ax^(2)+bx+c=0 has the roots alpha^(2)+beta^(3)+gamma^(4),beta...
Text Solution
|