Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT-TEMPERATURE AND THERMAL EXPANSION-All Questions
- The focal length of a spherical mirror is given by f=R/2 , where R is...
Text Solution
|
- Height of mercury in a barometer is h0 = 76. 0 cm at a temperature of ...
Text Solution
|
- In the last problem if the scale for reading the height of mercury col...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods of different metals having the same area of cross section A a...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods of equal cross-sections, one of copper and the other of stee...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that the coefficient of linear expansion of the material of a r...
Text Solution
|
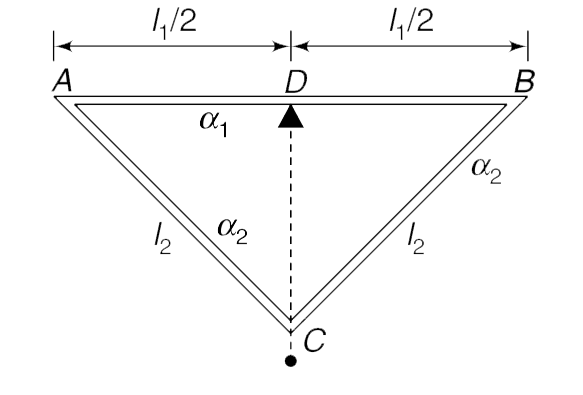
- In a compensated pendulum a triangular frame ABC is made using two dif...
Text Solution
|