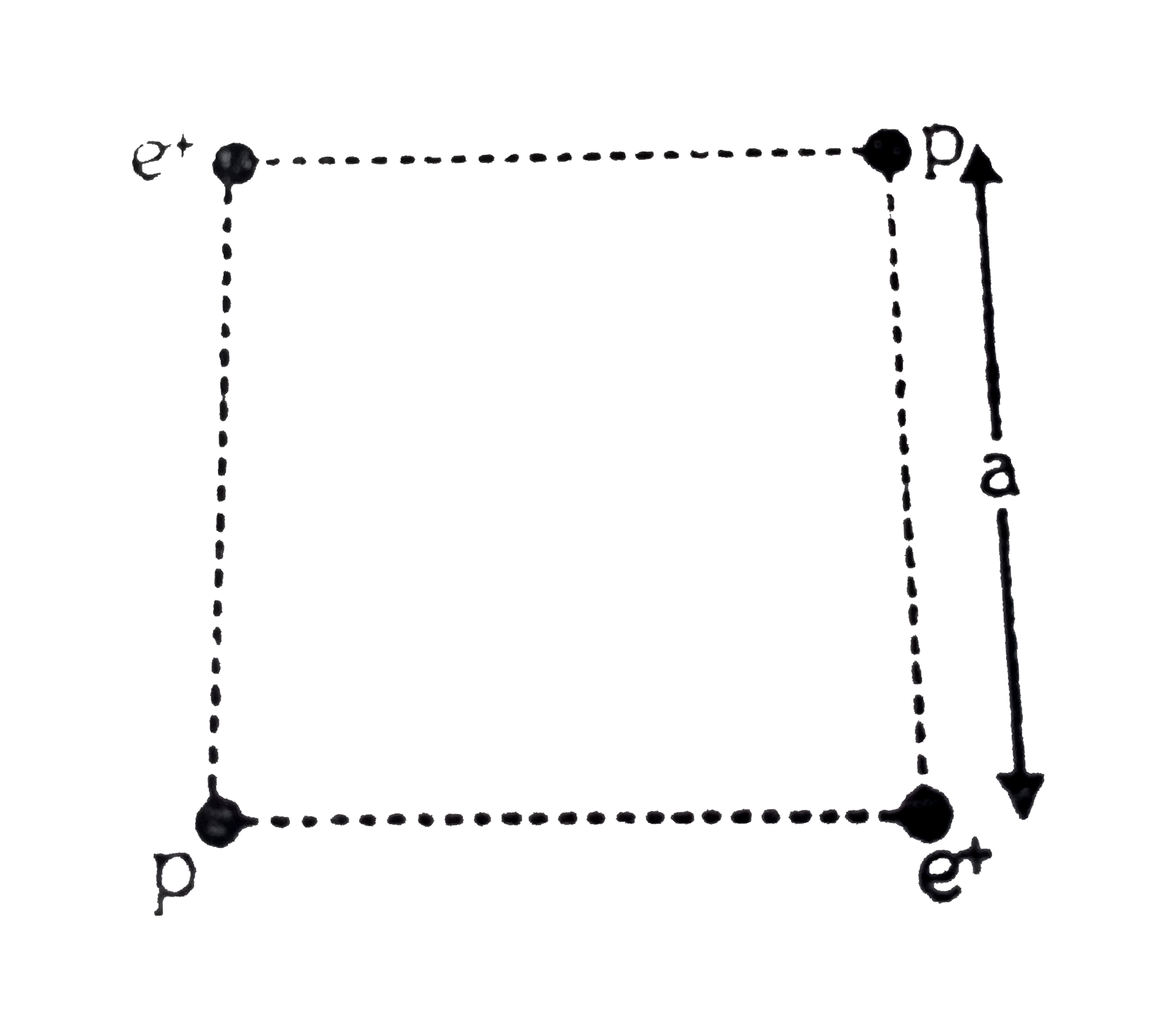
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise Part -II Example Some worked out Examples|1 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise-01|87 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise SUBJECTIVE QUESTION|9 VideosKINEMATICS (MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE AND MOTION IN A PLANE)
ALLEN|Exercise BEGINNER S BOX-7|8 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD, UNITS AND DIMENSIONS & ERRORS IN MEASUREMENT
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-IV|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-MISCELLANEOUS-Part -II Example
- Two conducting hollow spherical shells of radius R and 2R carry charge...
Text Solution
|
- An isolated conducting sphere of charge Q and radius R is connected to...
Text Solution
|
- Two positrons (e+) and two protons (p) are kept on four corners of a s...
Text Solution
|
- Four charges are placed at the circumference of a dial clock as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A small electric dipole is placed at origin with its dipole moment dir...
Text Solution
|
- Uniform electric field of magnitude 100 V//m in space is directed alon...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a uniformly charged hemisphere of radius R. It has a volu...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length I rotates at angular velocity omega about an...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a finite charged rod. Electric field at point P (shown) makes...
Text Solution
|
- The alectric potential in a region is given by the relation V(x)=4+5x^...
Text Solution
|
- A thin homogeneous rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate in ver...
Text Solution
|
- A thin homogeneous rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate in ver...
Text Solution
|
- A thin homogeneous rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate in ver...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum is suspended in a lift which is going up with an acc...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of potential with distance x from a fixed point is shown...
Text Solution
|
- The energy density u is plotted against the distance r from the centre...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shown four situations in which charges as indicated (q gt 0...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field is given by vec(E)=(yhat(i)+xhat(j))N/C. Find the wo...
Text Solution
|
- The arrangement shown consists of three elements. (i) A thin rod of ...
Text Solution
|
- Six charges are kept at the vertices of a regular hexagon as shown in ...
Text Solution
|