Potential at a height H on the axis of the disc V(P):
The charge dq contained in the ring shown in figure.
Potential of p due to this ring

`dV=1/(4pi epsilon_(0)).(dq)/x` where `x=sqrt(H^(2)+r^(2))`
`dV=1/(4pi epsilon_(0)).((2pirdr)sigma)/sqrt(H^(2)+r^(2))=(sigma/(2epsilon_(0)))xx((rdr)/sqrt(H^(2)+r^(2)))`
`:.` Potential due to the complete disc
`V_(p)=underset(r=0)overset(r=a)(int)dV=sigma/(2epsilon_(0)) underset(r=0)overset(r=a)(int)(rdr)/sqrt(H^(2)+r^(2))`
`V_(p)=sigma/(2epsilon_(0))[sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))-H]`
Potential at centre (O) will be `V_(O)=(sigmaa)/(2epsilon_(0)) :. H=0`
(i) Particle is released from P and just reaches point O. Therefore from conservation of mechanical energy.
Decrease in graviational potential energy
= Increase in electrostatic potential energy
`(DeltaKE=0` because `K_(1)=K_(f)=0`)
`:. mgh=q[V_(o)-V_(p)]rArr gH=(q/m)(sigma/(2epsilon_(0)))`
`[a-sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))+H]` ...(i)
`q/m=(4epsilon_(0)g)/sigma :. (qsigma)/(2epsilon_(0)m)=2g`
Substituting in Eq. (i), we get
`gH=2g [a+H-sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))]`
`rArr H/2=(a+H)-sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))`
`rArr sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))=a+H/2`
`rArr a^(2)+H^(2)=a^(2)+H^(2)/4+aHrArr 3/4 H^(2)=aH`
`rArr H=4/3a` and `H=0 :. H=(4/3)a`
(ii) Potential energy of the particle at height H=Electrostatic potential energy + gravitational potential energy
`:. U=qV+mgH`
Here V=Potential at height H
`U=(sigmaq)/(2epsilon_(0))[sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))-H]+mgH` ...(ii)
At equilibrium position `F=(-dU)/(dH)=0`
Differentialting Eq. (ii) w.r.t H
`rArr mg+sigmaq/(2epsilon_(0))[(1/2)(2H)1/sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))-1]=0`
`( :' (sigmaq)/(2epsilon_(0))=2mg)`
`:. mg+2mg[H/sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))-1]=0`
`rArr 1+(2H)/sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))-2=0rArr (2H)/sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))=1`
`rArr H^(2)/(a^(2)+H^(2))=1/4rArr 3H^(2)=a^(@)rArr H=a/sqrt(3)`
From Eq. (ii) we can write U-H equation as
`U=mg (2sqrt(a^(2)+H^(2))-H)`
(Parabolic variation)
`U=2 mga` at `H=0`
and `U=U_("min")=sqrt(3)mga` at `H=a/sqrt(3)`
therefore, `U-H` graph will be as shown.
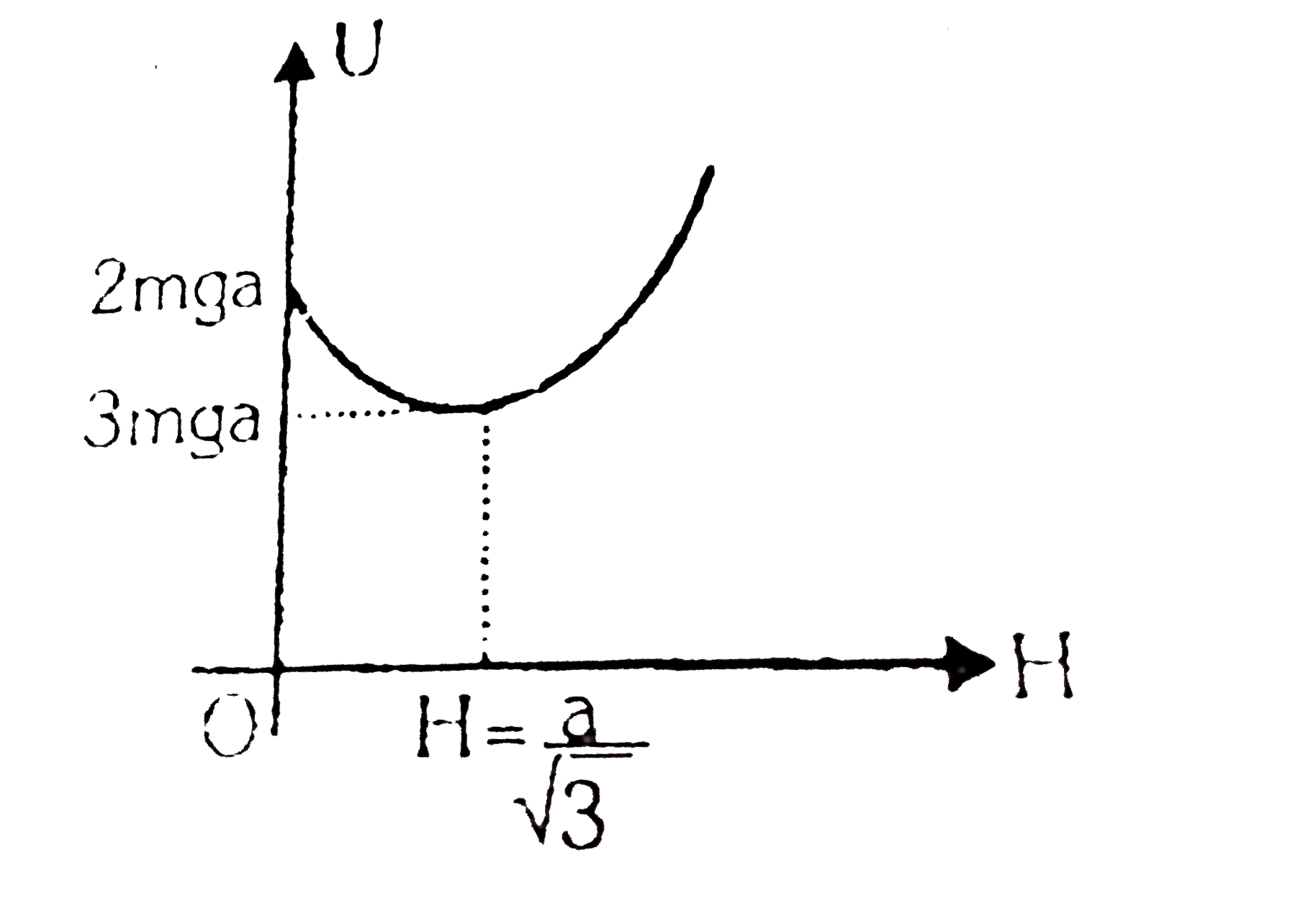
Note that at `H=a/sqrt(3)`, U is minimum.
Therefore, `H=a/sqrt(3)` is stable equilibrium position.

