Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Level 2
- Two ideal springs of same make (the springs differ in their lengths on...
Text Solution
|
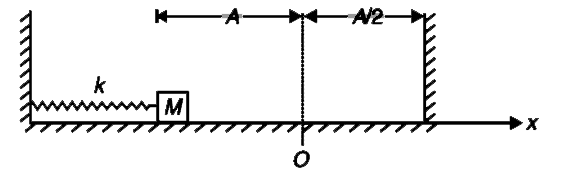
- A block of mass M connected to an ideal spring of force constant k lie...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M connected to an ideal spring of force constant k, is...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is constrained to move along a straight line. A a...
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral prism of mass m is kept on a smooth table between two i...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks rest on a smooth horizontal surface. They are connected by ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A (2 kg) and B (3 kg) rest on a smooth horizontal surface, ...
Text Solution
|
- A spring has force constant k = 200 N//m and its one end is fixed. The...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical simple pendulums A and B are fixed at same point. They a...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres A and B of the same mass m and the same radius are placed ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small blocks of mass m and 4m are connected to two springs as show...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M = 40 kg is released on a smooth incline from point A...
Text Solution
|
- Two tunnels - T(1) " and " T(2) are dug across the earth as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- The given figure shows the variation of the kinetic energy of a simple...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical small elastic balls have been suspended using two string...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of length L has a bob of mass m. The bob is connecte...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of mass m and length L is tied, at its end B, to a th...
Text Solution
|
- A railway tank wagon with its 2m diameter and 6m long horizontal cylin...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum consists of an inextensible thread connected to a solid sph...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius r is connected to a string of length L. The string is...
Text Solution
|