A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY BASICS
IIT-JEE PREVIOUS YEAR (CHEMISTRY)|Exercise Interger Answer Type Questions|1 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY BASICS
IIT-JEE PREVIOUS YEAR (CHEMISTRY)|Exercise CHAPTER TEST|2 VideosNUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
IIT-JEE PREVIOUS YEAR (CHEMISTRY)|Exercise CHEMISTRY|2 VideosP BLOCK ELEMENTS
IIT-JEE PREVIOUS YEAR (CHEMISTRY)|Exercise Topic 2|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
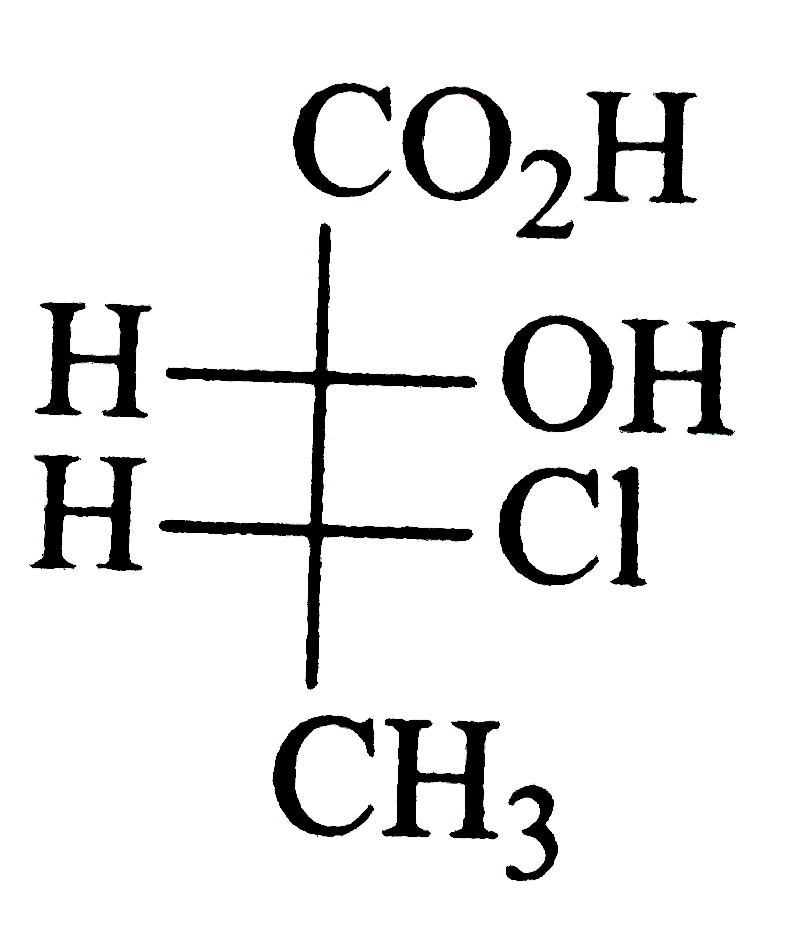 is
is