Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
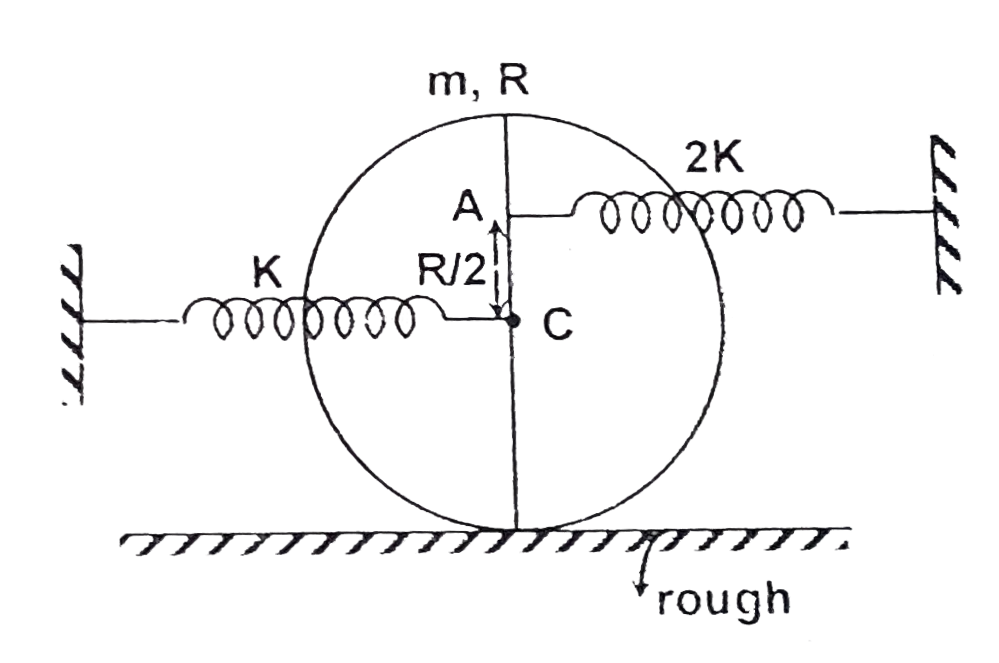
- A uniform circular disc of mass 'm' and radius 'R' is placed on a roug...
Text Solution
|
- From the circular disc of radius 4R two small discs of radius R are cu...
Text Solution
|
- Given a uniform disc of mass M and radius R . A small disc of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- A small hole is made in a disc of mass M and radius R at a distance R/...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m is attached to a spring of spring constant k ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass m and radius r placed on a routh horizontal surface. A ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc of mass 'm' and radius 'R' is placed on a roug...
Text Solution
|
- Find the centre of mass of a thin, uniform disc of radius R from which...
Text Solution
|
- One end of spring of spring constant k is attached to the centre of a ...
Text Solution
|