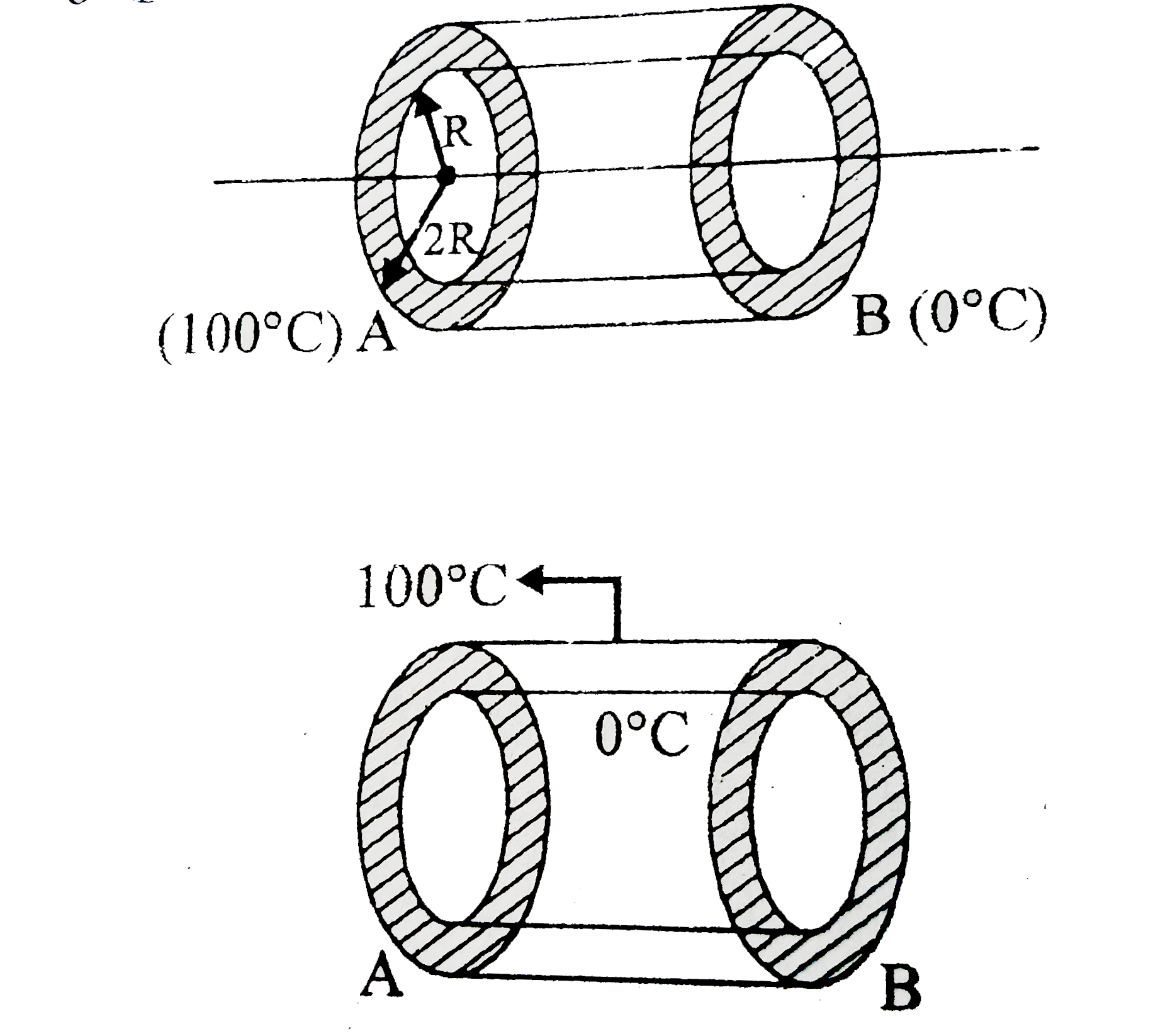A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- Block A is a 50-g aluminium block originally at 90^@C. Block B is a 10...
Text Solution
|
- The power emitted per unit area of a black body is R watt/m^2. At what...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure-II temperature of inner surface of cylinder is 0^@C and ...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel of volume 0.02m^3 contains a mixture of hydrogen and helium a...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel with open mouth contains air at 60^@C. When the vessel is hea...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains a mixture of one mole of oxygen and two moles of nit...
Text Solution
|
- The molar heat capacity C for an ideal gas going through a given proce...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas requires 207 J heat to raise the temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclic process is shown on the P-T diagram. Which of the curve shown...
Text Solution
|
- A given quantity of a ideal gas occupies a volume of 100 litres at 100...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid bar of mass M is supported symmetrically by three wires each o...
Text Solution
|
- A black plane surface at a constant high temperature Th, is parallel t...
Text Solution
|
- A wire having cross-sectional area S is attatched to wall on one side ...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of I(AA)/I(BB) will be (both are identical thin rods of leng...
Text Solution
|
- In the 1st figure shown here rod is massless and at its end a bob of m...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical disks, roll without sliding across a horizontal floor wi...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass m each are rotating parallel to xz plane in circ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass m each are rotating parallel to xz plane in circ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass m each are rotating parallel to xz plane in circ...
Text Solution
|
- A calorimeter contains 400 gm of water at temperature of 5^@C. Then, 2...
Text Solution
|