Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Level 3
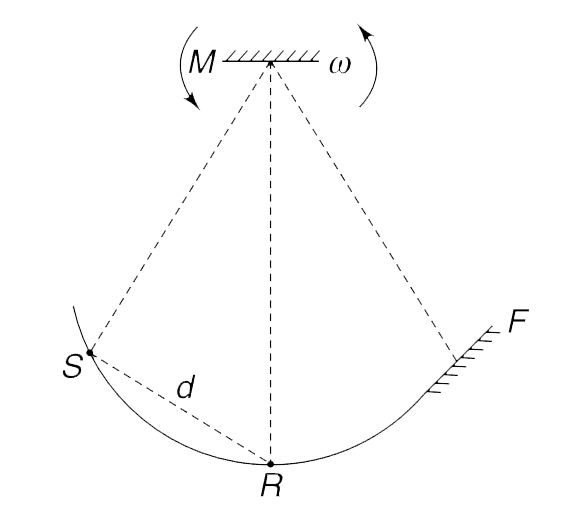
- A source of laser (S), a receiver (R) and a fixed mir- ror (F) – all l...
Text Solution
|
- In the Figure FE is a man of height H standing on a floor. E is eye of...
Text Solution
|
- An observer views his own image in a convex mirror of radius of curvat...
Text Solution
|
- The Figure (a) shows two media having refractive index mu and mu' with...
Text Solution
|
- A stick is placed inside a hemispherical bowl as shown in Figure. The ...
Text Solution
|
- The cross section of a prism is a regular hexagon. A narrow beam of li...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light is incident on a spherical drop of water (mu ...
Text Solution
|
- An isosceles right angled triangular glass (mu = 1.6) prism has a cavi...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light rays parallel to the principal axis (the x axis) a...
Text Solution
|
- O is a small object placed at a distance D from the eye E of an observ...
Text Solution
|