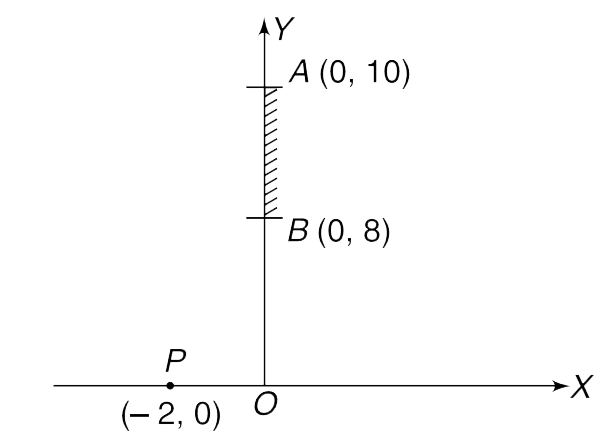
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Level 2
- Sunrays pass through a pinhole in the roof of a hut and produce an ell...
Text Solution
|
- A car is travelling at night along a highway shaped like a parabola wi...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in the Figure. The mirror AB forms image ...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors M1 and M2 of length d each are placed at right angle...
Text Solution
|
- Three plane mirrors are kept as shown in the Figure A point object (O)...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors are joined together as shown. Two point objects A an...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors M1 and M2 are inclined at 30° to the vertical. A poi...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the eye and the feet of a boy is 1.5 m. He is sta...
Text Solution
|
- OP is the principal axis of a concave mirror M1. Just below the axis a...
Text Solution
|
- A real object AB has its image as IM when placed in front of a spheric...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical concave mirrors of equal focal length are put against ea...
Text Solution
|
- A long rectangular strip is placed on the principal axis of a concave ...
Text Solution
|
- A pencil (AB) of length 20 cm is moving along the principal axis of a ...
Text Solution
|
- A small object of height h is placed perpendicular to the principal ax...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a large parabolic mirror whose section can be represented by ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a glass (mu(g) = 1.5) vessel, partly filled with water (...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors M1 and M2, placed at right angles, form two sides of...
Text Solution
|
- When the sun appears to be just on horizon, it is in fact below the ho...
Text Solution
|
- Intensity of a light beam can be defined as amount of light energy inc...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram shown, a light ray is incident on the lower medium boun...
Text Solution
|