Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
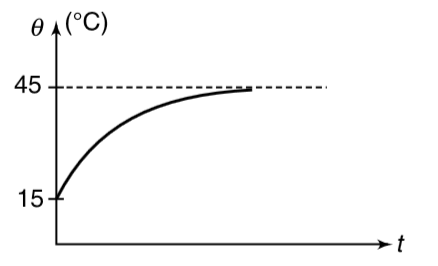
- A metal ball of mass 1.0 kg is kept in a room at 15^(@)C. It is heated...
Text Solution
|
- A metal ball of mass 1kg is heated by means of a 20W heater in a room ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal ball of mass 2kg is heated means of a 40W heater in a room at ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal ball of mass 2kg is heated means of a 40W heater in a room at ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal ball of mass 1.0 kg is kept in a room at 15^(@)C . It is heate...
Text Solution
|
- A block is kept in a room which is at 20^(@)C . To raise the temperatu...
Text Solution
|
- A metal cylinder of mass 0.5 kg is heated electrically by a 12 W heate...
Text Solution
|
- A metal bal of mass 1 kg is heated by means of a 20 W heater in a room...
Text Solution
|
- A metal ball of 1kg mass is heated by a 20W heater in a room at 20^(@)...
Text Solution
|