Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-MASTER PRACTICE PROBLEM-Subjective
- A man of mass 50 kg is standing on one end of a stationary wooden plan...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical rod of mass 4 kg is hanging on a rope and a 3kg cat is gras...
Text Solution
|
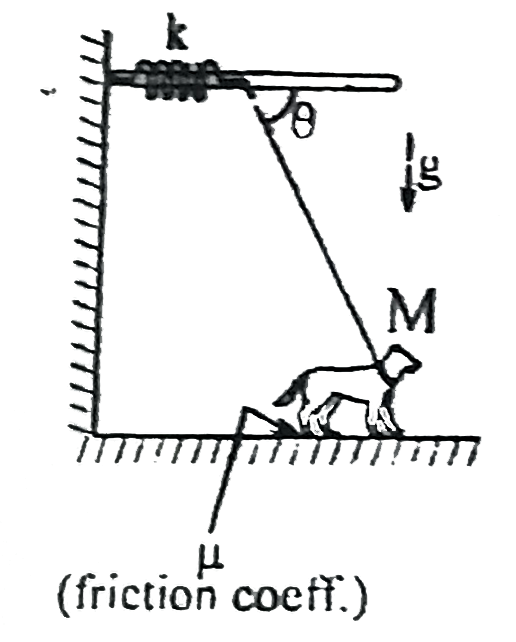
- A dog with mass M has its string attached to one end of a spring which...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a block placed on a bracket. Bracket is placed on a smoot...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical cubes of mass 1.5 M each are kept almost touching the fa...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of mass m=1kg can slide over a smooth vertical rod. A light str...
Text Solution
|
- A man of height h(0)=2 m is bungee jumping from a platform situated a...
Text Solution
|
- At what angle theta(0) with the horizontal, should a shell be fired if...
Text Solution
|
- Two beads connected by a light inextensible string are placed over fix...
Text Solution
|
- An object A of mass 2 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal track ...
Text Solution
|
- A cart of mass M has a pole on it from which a ball of mass mu hangs ...
Text Solution
|
- Neglecting friction at the axle and the inertia of the two step pulley...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform stick of mass m and length l with I=1/12 ml^(2) spins around...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal masses are situated at a separation r(0) One of them is imp...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical planet has uniform density pi/2xx10^(4)kg//m^(3). Find out...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass 'm' and 3 m are initially at rest an infinite di...
Text Solution
|
- Two objects of equal volume V=1 m^(3) and different densities d(1) =50...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a pond full of water having the shape of a truncated ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of wood weights 16 kg in air. A lead block which has apparent ...
Text Solution
|
- Water (density 1 gm//c) is to be sucked upto point A. The area of the ...
Text Solution
|