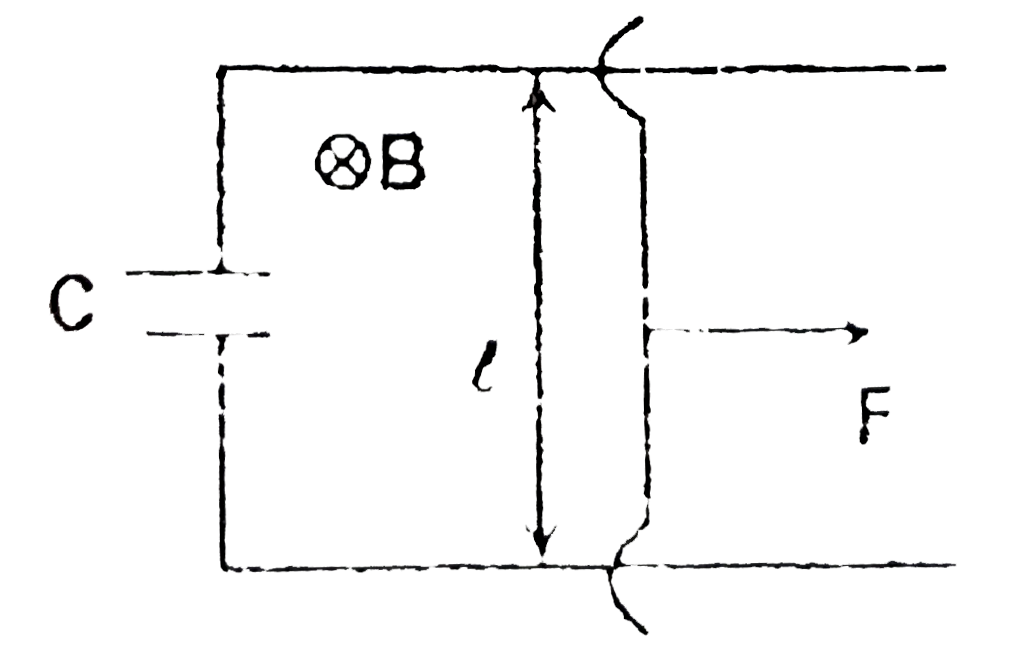
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-GMP ASSESMENT-Multiple Question
- A circular loop of radius r, having N turns of a wire, is placed in a ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular loop of radius a and resistance R palced perpendicu...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire of length l and mass m can slide without friction on...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin slabs of refractive indicies mu(1) and mu(2) are placed parll...
Text Solution
|
- A bi-convex lens is placed between a light source and a concave mirror...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves towards a concave mirror of focal length 30cm along i...
Text Solution
|
- Young's double-slit experiment is conducted in water (mu(1)) as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid transparent sphere made of glass (R.I.=mu gt 1) has a small, o...
Text Solution
|
- A luminous point object is placed at O, whose image is formed at I as ...
Text Solution
|
- When photons of energy (hc)/(lamda) fall on a metal surface, photoelec...
Text Solution
|
- The threshold wavelength for photoelectric emission for a material is ...
Text Solution
|
- Photoelectric effect supports quantum nature of light because (a) th...
Text Solution
|
- When photons of energy 4.25 eV strike the surface of metal A, the ejec...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a r...
Text Solution
|
- Threshold wavelength of certain metal is lamda0 A radiation of wavelen...
Text Solution
|
- A frame a bed and a sliding rod PQ of resistance R, start moving with ...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres A and B have the same radii but the capacity of A is grea...
Text Solution
|
- A canon of mass M is mounted on an east west frictionless railway trac...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is launched from a height 8R above the surface of earth and...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB of mass M and length L lies on smooth horizontal table impuls...
Text Solution
|