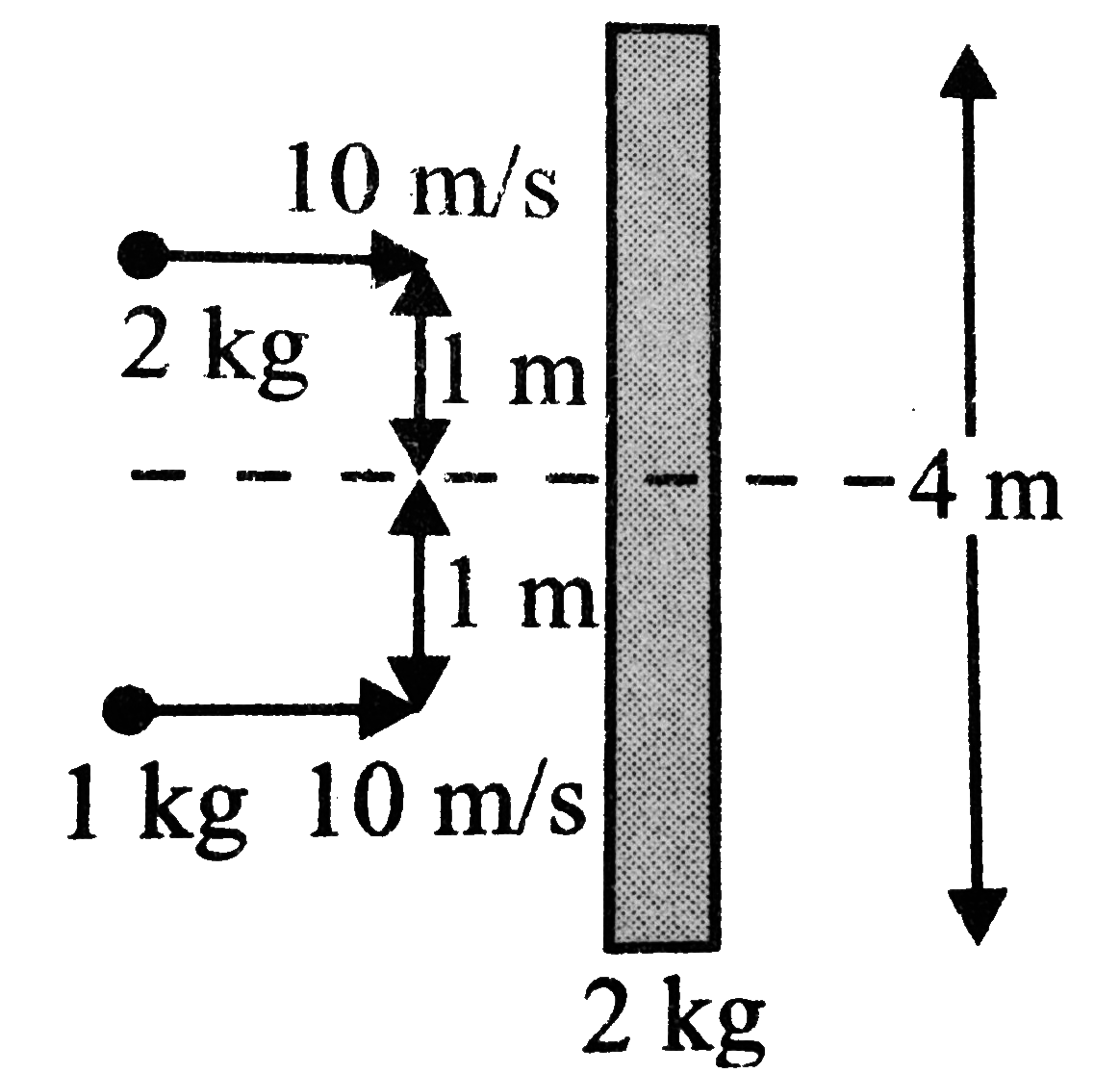
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-GMP ASSESMENT-Comprehension
- 4 identical balls of radius R and mass m are lying a gravity free spac...
Text Solution
|
- 4 identical balls of radius R and mass m are lying a gravity free spac...
Text Solution
|
- A Iong slender rod of mass 2 kg and length m is placed on a smooth hor...
Text Solution
|
- A Iong slender rod of mass 2 kg and length m is placed on a smooth hor...
Text Solution
|
- A Iong slender rod of mass 2 kg and length m is placed on a smooth hor...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of mass M moving with initial velocity u collides ela...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of mass M moving with initial velocity V collides ela...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of mass M moving with initial velocity V collides ela...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows 4 identical masses of mass m, arranged on a cube as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows 4 identical masses of mass m, arranged on a cube as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows 4 identical masses of mass m, arranged on a cube as shown...
Text Solution
|
- The word fluid means a substance having particles which readily of its...
Text Solution
|
- The word fluid means a substance having particles which readily of its...
Text Solution
|
- The word fluid means a substance having particles which readily of its...
Text Solution
|
- When we raise the temperature of a body, the molecules and atoms move ...
Text Solution
|
- When we raise the temperature of a body, the molecules and atoms move ...
Text Solution
|
- When we raise the temperature of a body, the molecules and atoms move ...
Text Solution
|
- A beaker containing an ideal fluid executes plane SHM in a horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A beaker containing an ideal fluid executes plane SHM in a horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A beaker containing an ideal fluid executes plane SHM in a horizontal ...
Text Solution
|