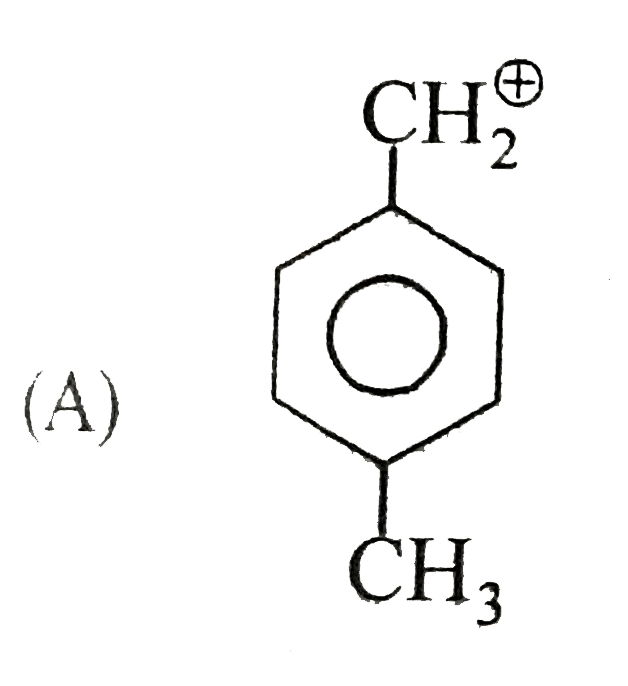
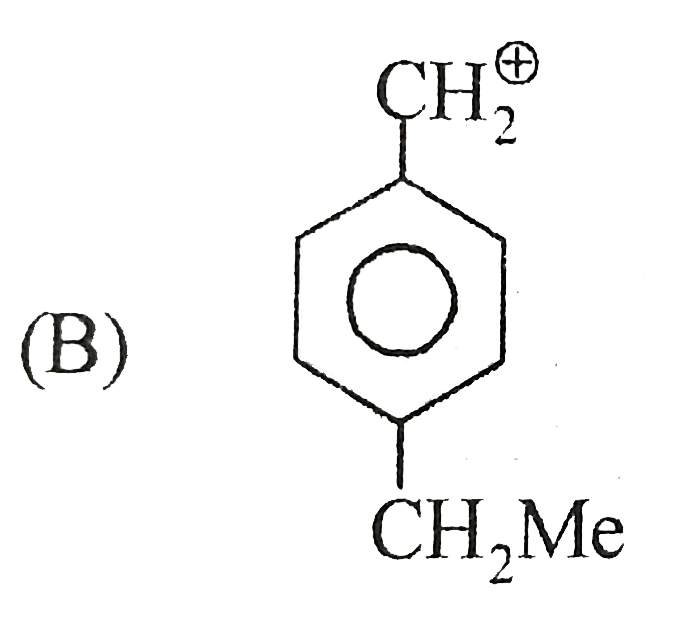
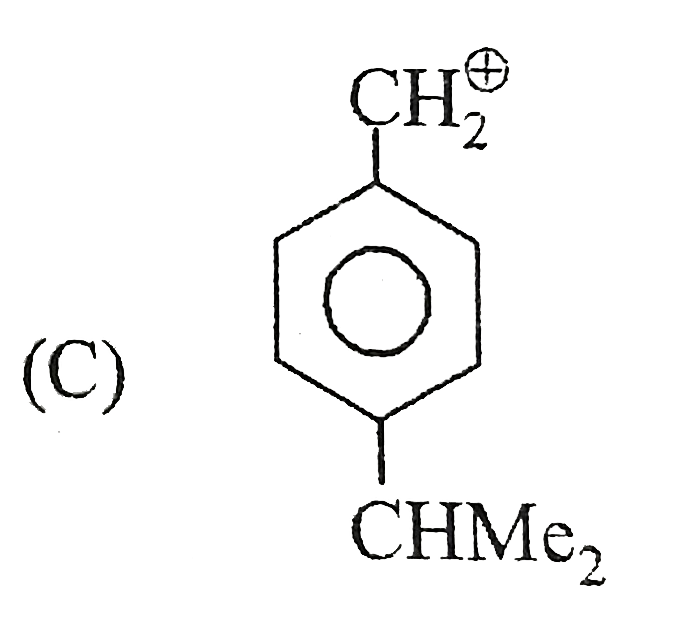
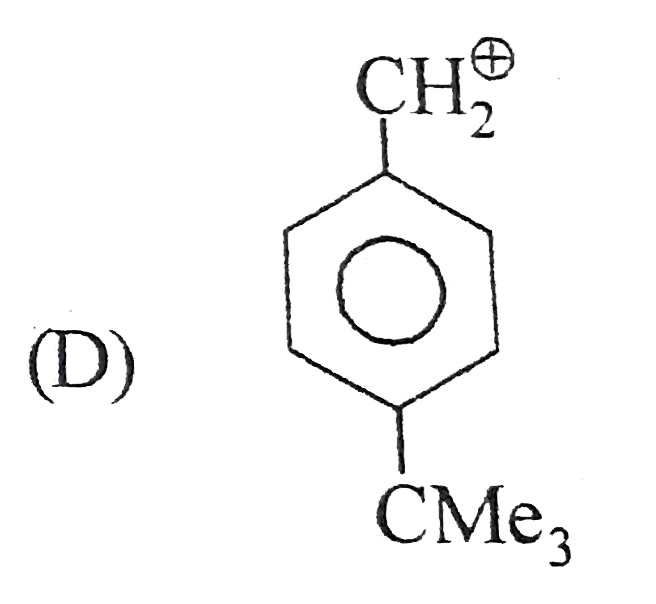
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
BANSAL|Exercise Exercise 2|38 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
BANSAL|Exercise Exercise 3|19 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
BANSAL|Exercise Exercise 3|19 VideosD AND F BLOCK ELEMENTS
BANSAL|Exercise EXERCISE-4 (SECTION-B)|7 VideosNITROGEN COMPOUNDS
BANSAL|Exercise EXERCISE-4 (Section-4) SECTION -B( JEE Main Previous Question )|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Exercise 1
- In which of the following molecules pi-electron density in ring is min...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has longest C-O bond
Text Solution
|
- Select the least stble resonating structure in each of the following s...
Text Solution
|
- Select the most stable intermediate
Text Solution
|
- Write correct order regarding stability of intermediates (I). CH(2)=...
Text Solution
|
- Rate of abstraction of iodine by Ag^(o+) is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following alkene is most stable alkene.
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is lowest pKa value?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will give effervesce of CO(2) with NaHCO(3)
Text Solution
|
- Select the one which does not results in the formation of aromatic spe...
Text Solution
|
- Correct order of stability of these carbocatios is:
Text Solution
|
- Correct order of stability-
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is a+I group
Text Solution
|
- Correct order of heat of combustion for following compounds is: (P) ...
Text Solution
|
- Compare rotational energy barrier for indicated bond.
Text Solution
|
- The carbocation (CH(3))(3)C^(+) is stabilized primarily by
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compound is most basic
Text Solution
|
- Correct order for basic strength.
Text Solution
|
- Arrange following increasing order of stability
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is relatively most stable carbocation?
Text Solution
|