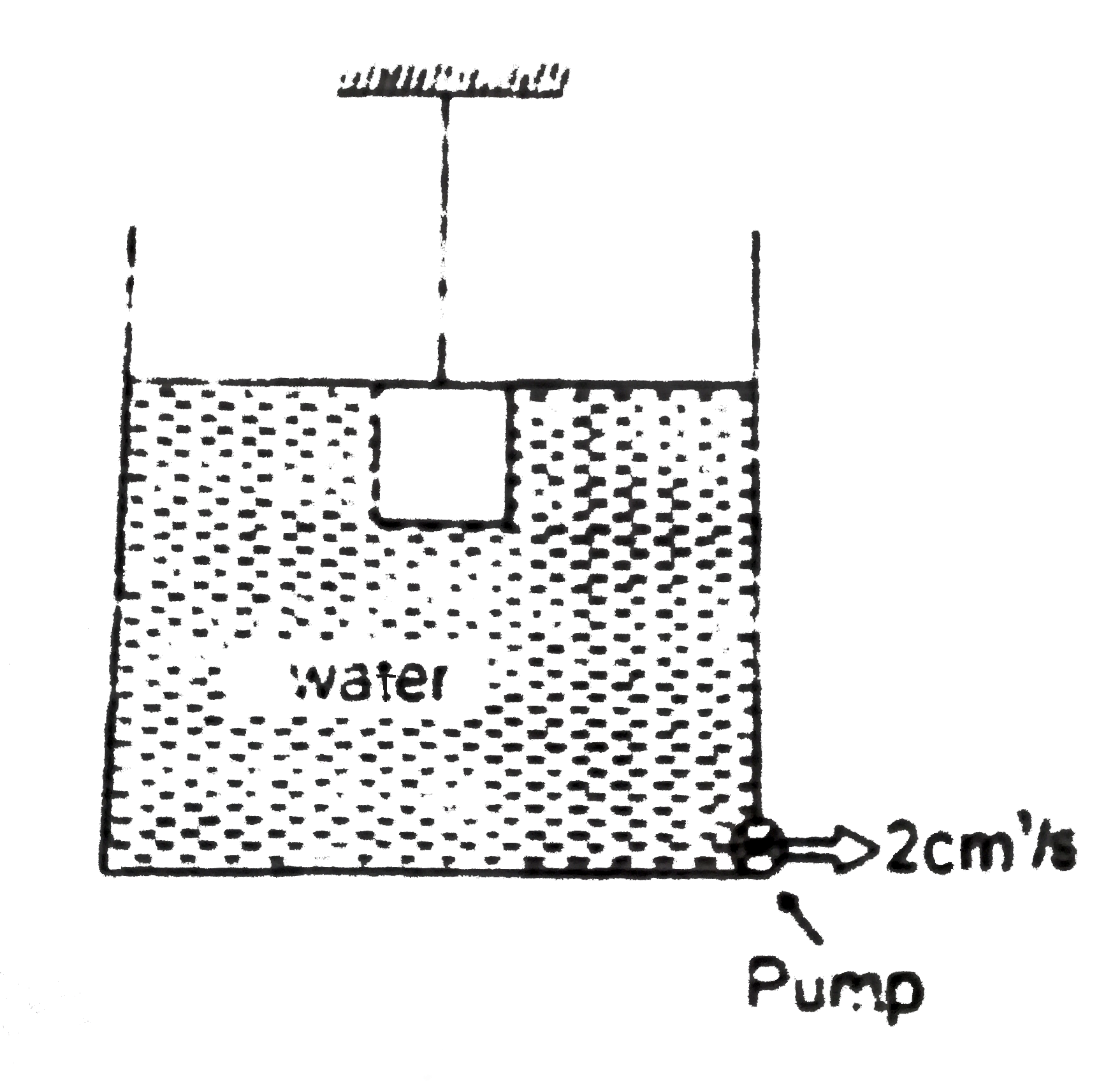
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-FLUID MECHANICS-Exercise- 2 PART - II
- A closed tube in the form of an equilateral triangle of side l contain...
Text Solution
|
- An open tank 10 m long and 2m deep is filled upto height 1.5 m of oil ...
Text Solution
|
- A stick of square cross-section (5 cm xx 5 cm) and length '4m' weighs ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a cubical block of side 10 cm and relative density 1.5 su...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical vessel filled with water upto a height of 2m stands on h...
Text Solution
|
- A tank containing gasoline is sealed and the gasoline is under pressur...
Text Solution
|
- A large open top container of negligible mass and uniform cross-sectio...
Text Solution
|
- A non-viscous liquid of constant density 1000kg//m^3 flows in a stream...
Text Solution
|
- Water shoots out of a pipe and nozzle as shown in the figure. The cros...
Text Solution
|