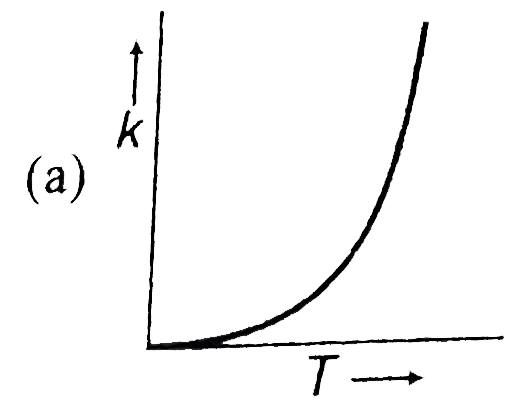
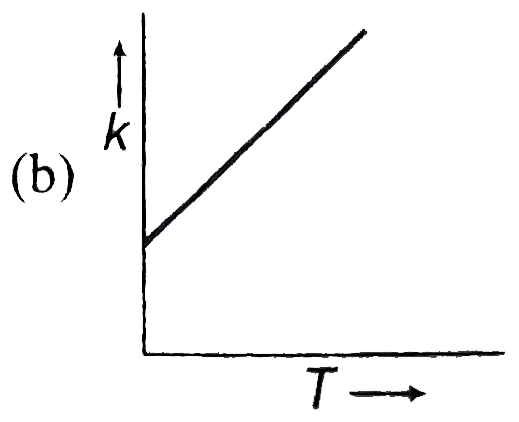
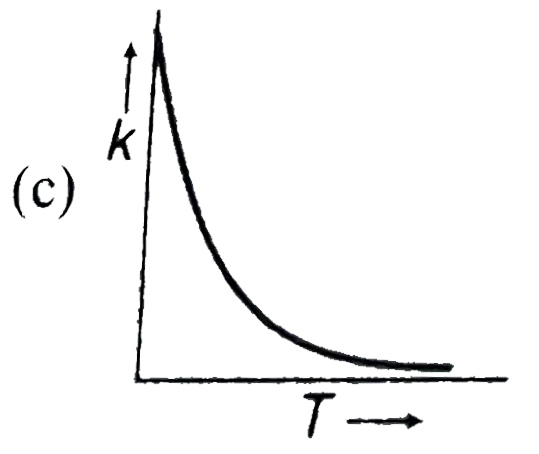
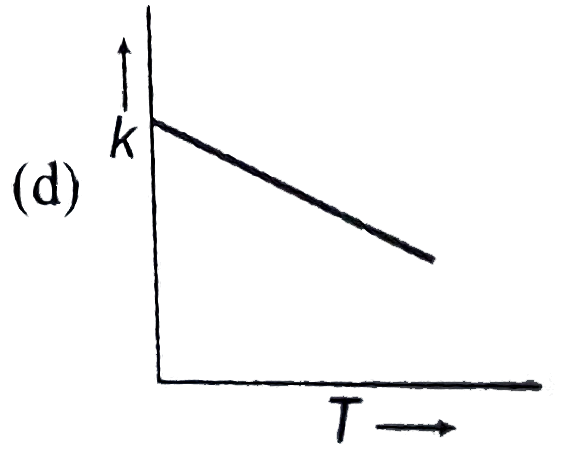
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IIT-JEE PREVIOUS YEAR (CHEMISTRY)-CHEMICAL KINETICS-JEE Main And Advanced
- In the reaction, P+Q rarr R+S the time taken for 75% reaction of P i...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of a reaction doubles when its temperature changes form 300 K...
Text Solution
|
- Plots showing the variation of the rate constant (k) with temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A rarr P, the temperature (T) dependent rat...
Text Solution
|
- Under the same reaction conditions, the intial concentration of 1.386 ...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder a reaction aG+bH rarr Products. When concentration of both th...
Text Solution
|
- which one of the following statements (s) in incorrect about order of ...
Text Solution
|
- A follows first order reaction. (A) rarr Product The concentration...
Text Solution
|
- In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant decreases...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder the chemical reaction N(2)(g) + 3H(2)(g) rarr 2NH(3)(g) T...
Text Solution
|
- If I is the intenisty of an absorbed light and c is the concentration ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for the reaction, 2N(2)O(5) rarr 4NO(2) + O(2) is 3....
Text Solution
|
- The half- life periof of a radioactive element is 140 days. After 560 ...
Text Solution
|
- A catalyst is a substance which
Text Solution
|
- The specific rate constant of a first order reaction depends on the
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of a reaction depends on
Text Solution
|
- According to the Arrhenius equctions
Text Solution
|
- For the first order reaction 2N(2)O(5)(g) rarr 4NO(2)(g) + O(2)(g)
Text Solution
|
- the following statement (s) is are correct
Text Solution
|
- A catalyst
Text Solution
|