A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS -VECTORS-Exercise
- A vector vec(a) is turned without a change in its length through a sma...
Text Solution
|
- Find the resultant of the three vectors vec(OA), vec(OB) and vec(OC) s...
Text Solution
|
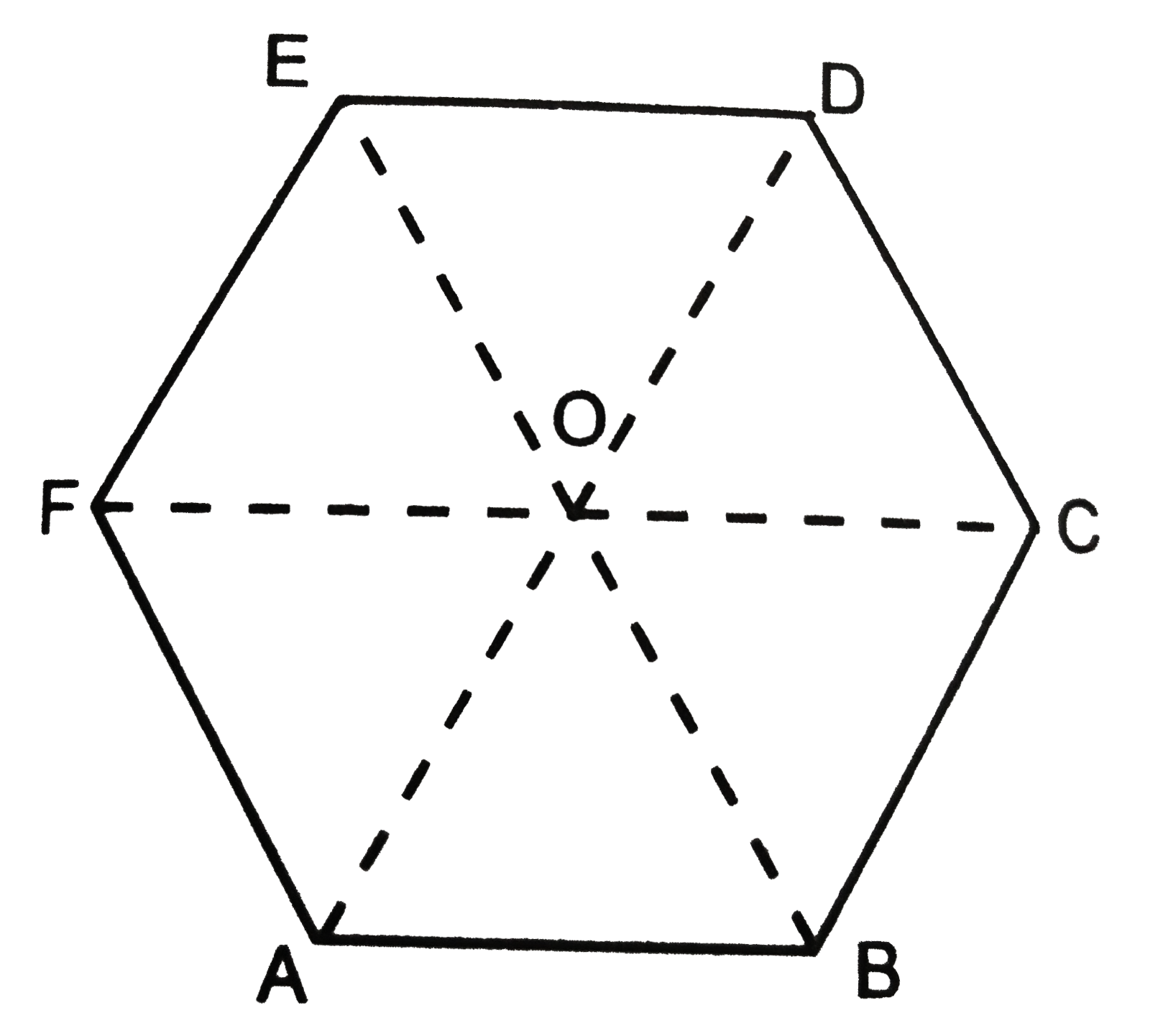
- ABCDEF is a regular hexagon, Fig. 2 (c ) .65. What is the value of ...
Text Solution
|
- The length of second's hand in watch is 1 cm. The change in Velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves towards east with velocity 5m//s. After 10 seconds it...
Text Solution
|
- A force F=-K(yhati+xhatj) (where K is a positive constant) acts on a p...
Text Solution
|
- The vectors from origin to the points A and B are vecA=3hati-6hatj+2ha...
Text Solution
|
- A metal sphere is hung by a string fixed to a wall. The sphere is push...
Text Solution
|
- A boat having a speed of 5km//hr. in still water, crosses a river of w...
Text Solution
|
- A man crosses a 320m wide river perpendicular to the current in 4 min....
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: vecAxxvecB is perpendicular to both vecA+vecB as well as ve...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Angle between hati+hatj and hati is 45^(@). Reason: hati...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: If theta be the angle between vecA and vecB then tan theta=...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1:If ,|vec A+vec B| =|vecA-vecB| then angle between vecA an...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Vector product of two vectors is an axial vector. Reason:...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Minimum number of non-equal Vectors in a plane required to ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Relative velocity of A w.r.t B is greater than the velocity...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Vector addition of two vectors vedA and vecB is commutative...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: vecA.vecB=vecB.vecA Reason: Dot product of two vectors is...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: vectau=vec(r)xxvec(F) and vectau!=vec(F)xxvec(r ) Reason:...
Text Solution
|
 .
.