A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS -WORK, ENERGY, POWER & COLLISION-Assertion
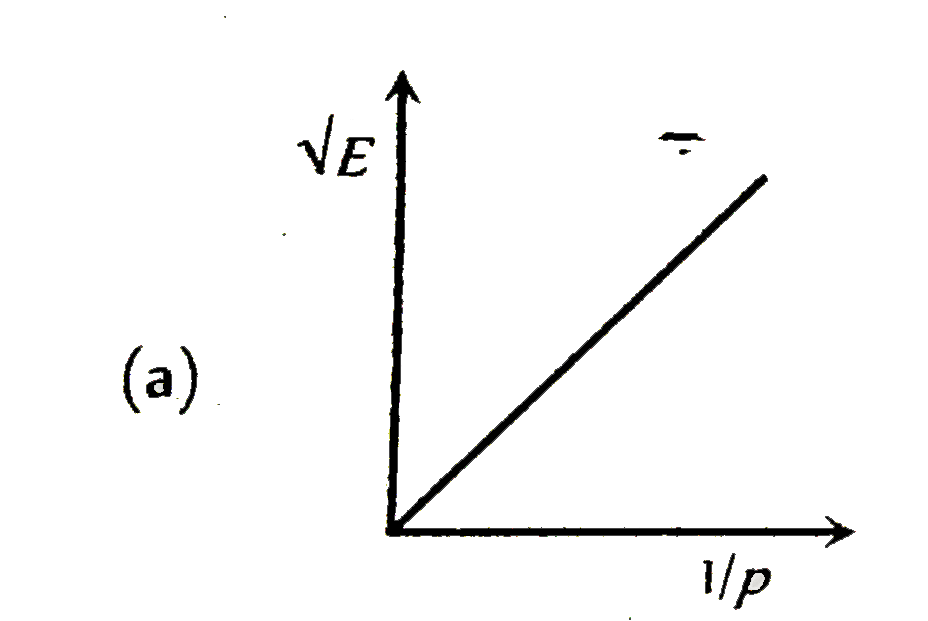
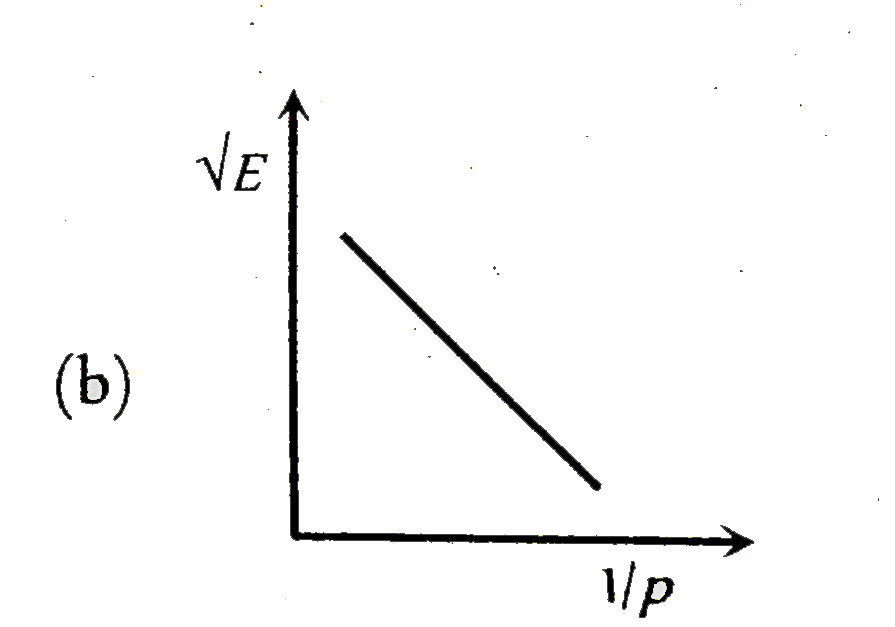
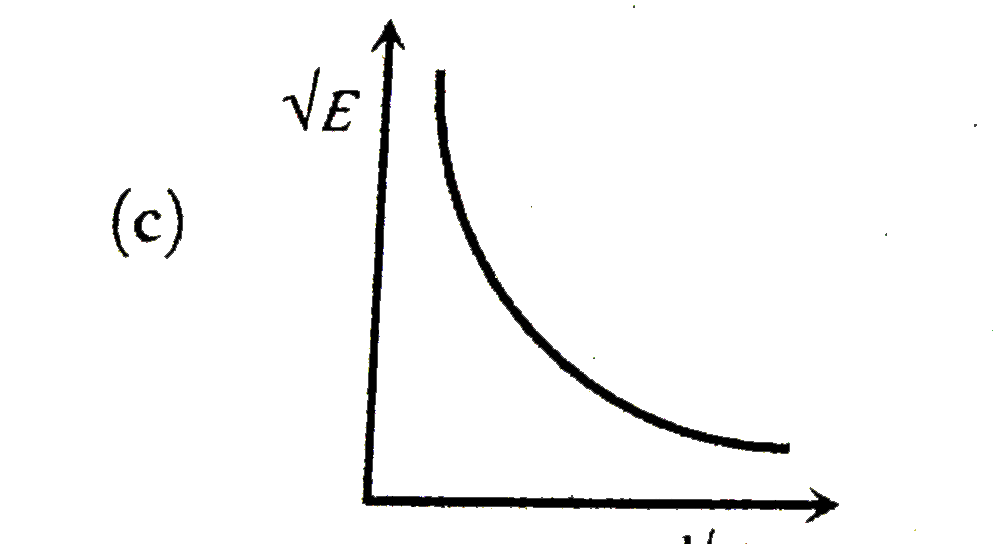
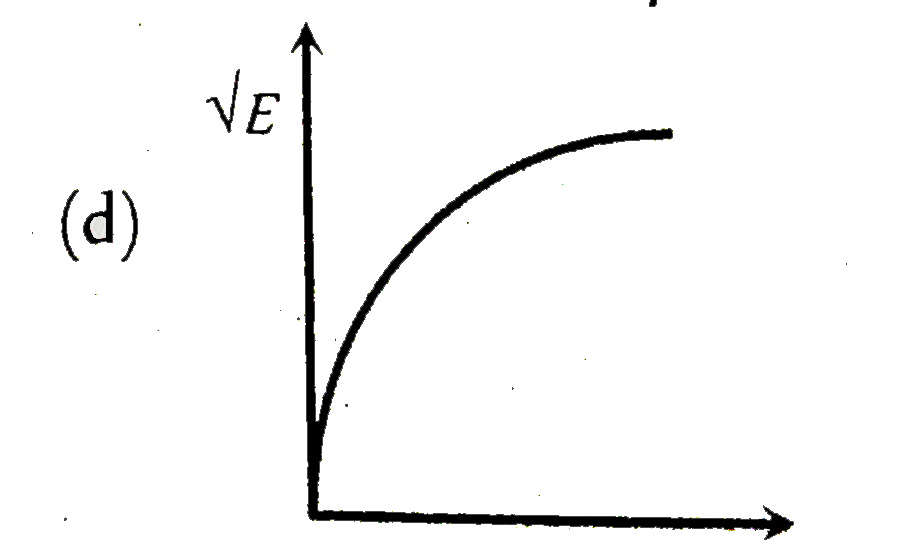
- The graph betwee sqrt(E) and (1)/(p) is (E=kinetic energy and p= momen...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: A person walking on a horizontal road with a load on his ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The work done during a round trip is always zero. Reaso...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Work done by friction on a body sliding down an inclined...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : When a gas is allowed to expand, work done by gas is pos...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A light body and a heavy body have same momentum. Then they...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The instantaneous power of an agent is measured as the dot...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The change in kinetic energy of a particle is equal to the ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A spring has potential energy , both when it is compressed ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1:Comets move around the sun in elliptical orbits, the gravi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Internal forces cannot change linear momentum. Reason: In...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Water at the foot of the water fall is always at differe...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The power of a pump which raises 100 kg of water in 10...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: According to law of conservation of mechanical energy chang...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : When the force retards the motion of a body, the work do...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: In an elastic collision of two bodies , the momentum and en...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A body cannot have energy without possessing momentum but...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Power developed in circular motion is always zero. Reas...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A kinetic energy of a body is quadrupled, when its veloc...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A quick collision between two bodies is more violent that s...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Work done by or against gravitational force in moving a b...
Text Solution
|