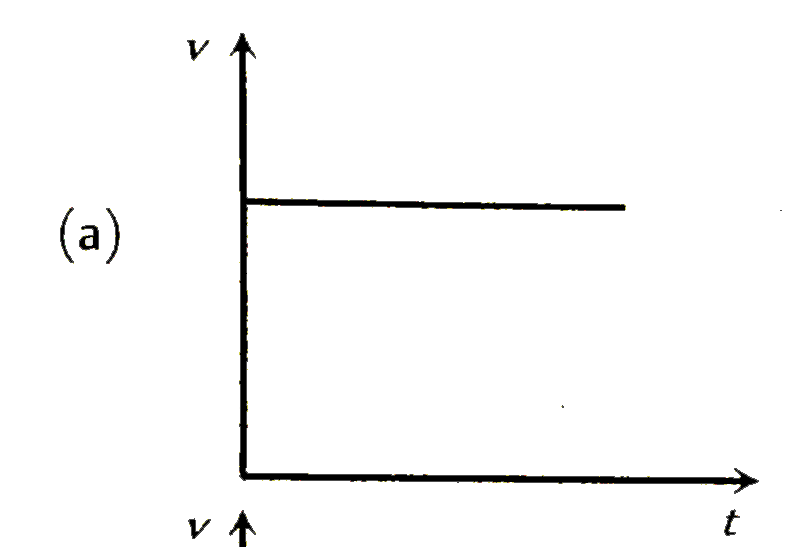
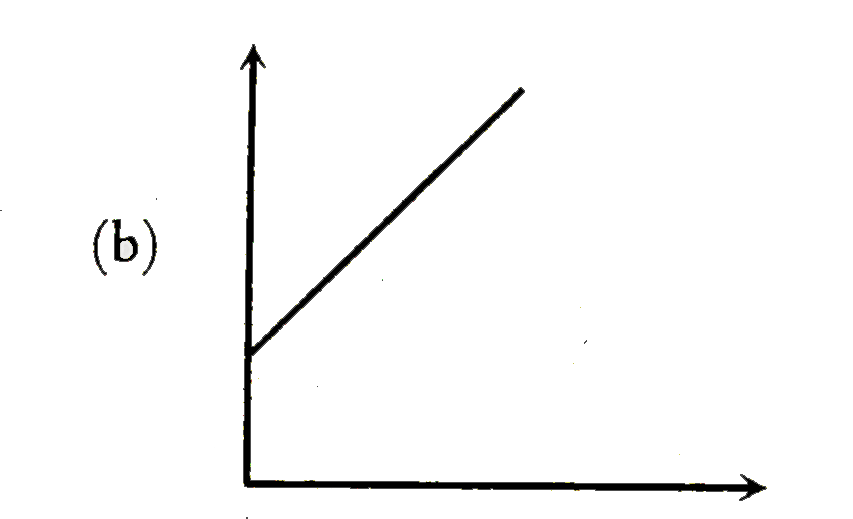
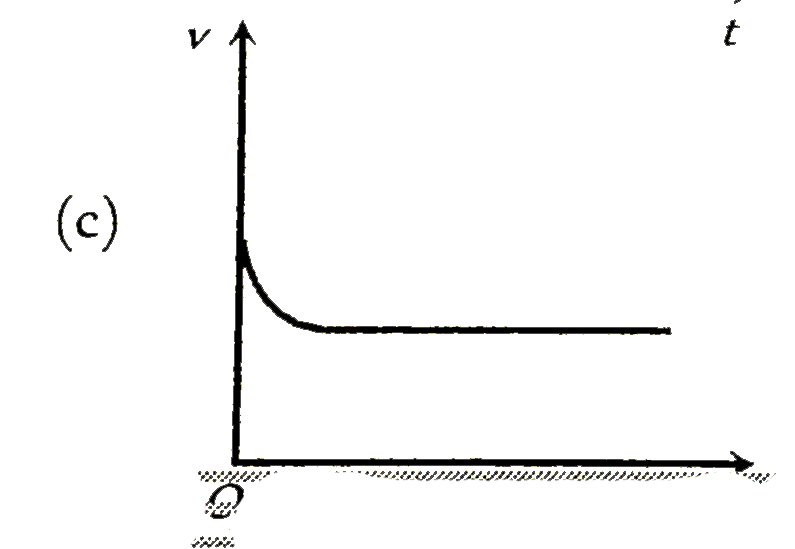
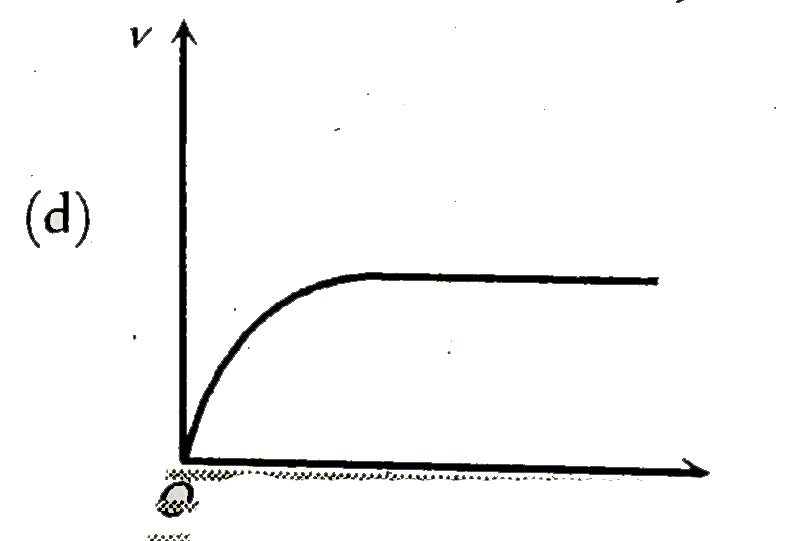
To determine the variation of velocity \( v \) with time \( t \) for a small spherical body falling vertically in a long column of viscous liquid, we can analyze the motion based on the principles of fluid mechanics, particularly Stokes' law.
### Step-by-Step Solution:
1. **Understanding the Forces Acting on the Sphere**:
- When a small spherical body falls through a viscous fluid, it experiences three main forces:
- **Weight (W)**: The gravitational force acting downwards, given by \( W = mg \), where \( m \) is the mass of the sphere and \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity.
- **Buoyant Force (B)**: The upward force exerted by the fluid, given by Archimedes' principle. For a sphere of volume \( V \), \( B = \rho_f V g \), where \( \rho_f \) is the density of the fluid.
- **Drag Force (F_d)**: The resistance force exerted by the fluid, which according to Stokes' law is given by \( F_d = 6 \pi \eta r v \), where \( \eta \) is the viscosity of the fluid, \( r \) is the radius of the sphere, and \( v \) is the velocity of the sphere.
2. **Setting Up the Equation of Motion**:
- As the sphere falls, it accelerates until the drag force equals the net downward force (weight minus buoyant force). At this point, the sphere reaches its terminal velocity \( v_t \).
- The equation can be set up as follows:
\[
mg - \rho_f V g - 6 \pi \eta r v = 0
\]
- Rearranging gives:
\[
mg - \rho_f V g = 6 \pi \eta r v
\]
3. **Identifying Terminal Velocity**:
- The terminal velocity \( v_t \) is reached when the net force acting on the sphere becomes zero. Thus, we can express terminal velocity as:
\[
v_t = \frac{(mg - \rho_f V g)}{6 \pi \eta r}
\]
- This indicates that the terminal velocity is constant and does not change with time once reached.
4. **Graphical Representation**:
- Initially, as the sphere starts falling, its velocity increases due to the net force acting on it. However, as it accelerates, the drag force increases until it balances the weight of the sphere, leading to a constant velocity.
- Therefore, the graph of velocity \( v \) versus time \( t \) will show an initial increase in velocity, which will then level off to a constant value (the terminal velocity).
5. **Conclusion**:
- The correct curve that represents this scenario will start at zero, rise steeply at first, and then flatten out as it approaches the terminal velocity. This indicates that the velocity increases with time until it reaches a constant value.