A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GRB PUBLICATION-GASEOUS STATE-Exercise
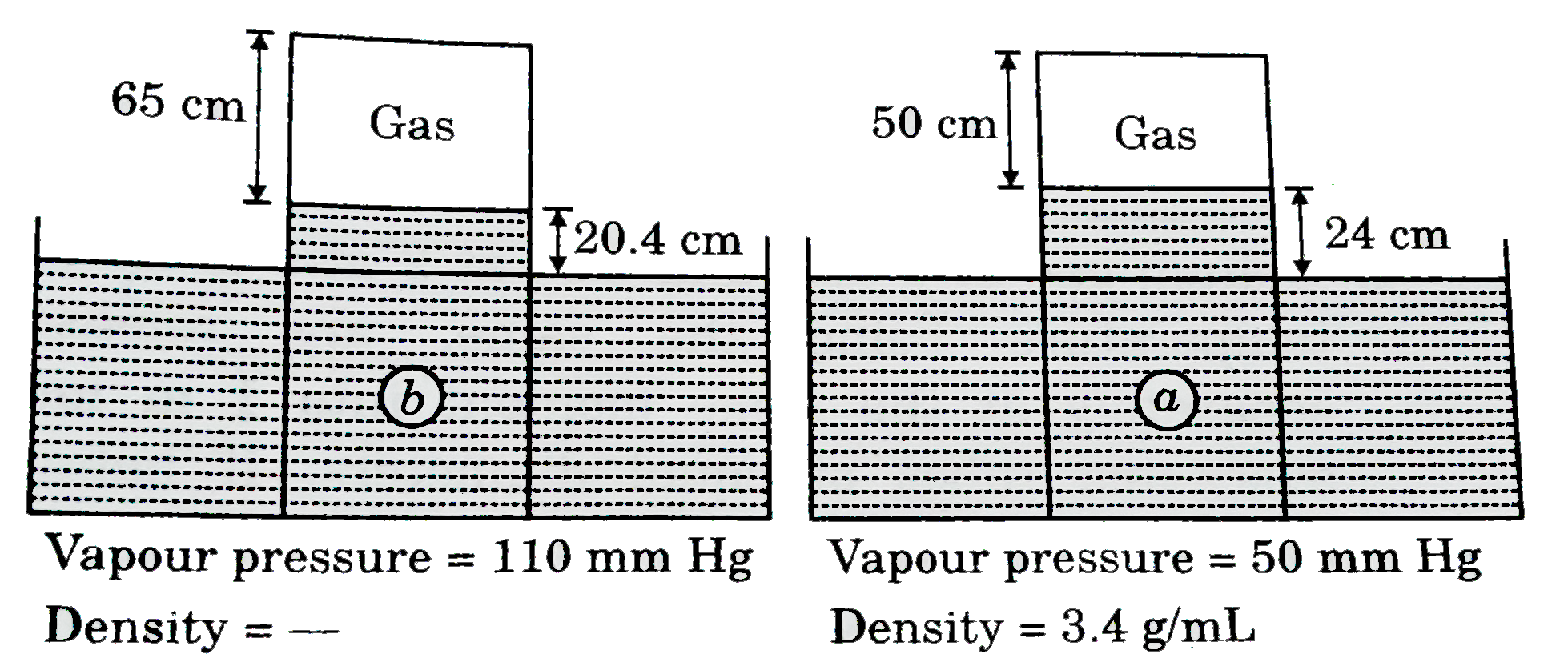
- If same amount of gas is trapped over liqquid (a) and liquid (b) in fo...
Text Solution
|
- If same amount of gas is trapped over liquid (a) and liquid (b) in fol...
Text Solution
|
- If same amount of gas is trapped over liquid (a) and liquid (b) in fol...
Text Solution
|
- Equal masses (W gram each) of three non- reacting gases X,Y and Z were...
Text Solution
|
- Equal masses (W gram each) of three non- reacting gases X,Y and Z were...
Text Solution
|
- Equal masses (W gram each) of three non- reacting gases X,Y and Z were...
Text Solution
|
- The constant motion and high velocities of gas particles lead to some ...
Text Solution
|
- The constant motion and high velocities of gas particles lead to some ...
Text Solution
|
- The constant motion and high velocities of gas particles lead to some ...
Text Solution
|
- For a non-ideal gas, the compressibility factor (Z) is defined as Z=...
Text Solution
|
- For a non-ideal gas, the compressibility factor (Z) is defined as Z=...
Text Solution
|
- Ideal gas is defined as a gas whose molecules move independent of each...
Text Solution
|
- Ideal gas is defined as a gas whose molecules move independent of each...
Text Solution
|
- Two bulbs 'X' and 'Y' of equal volumes are connected through a stop co...
Text Solution
|
- Two bulbs 'X' and 'Y' of equal volumes are connected through a stop co...
Text Solution
|
- The process by which a gas passes through a small hole into vacuum is ...
Text Solution
|
- The process by which a gas passes through a small hole into vacuum is ...
Text Solution
|
- A container is divided into two compartments. One compartment contains...
Text Solution
|
- A container is divided into two compartments. One compartment contains...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows initial conditions of a uniform cylinder with frictio...
Text Solution
|