Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GRB PUBLICATION-GASEOUS STATE-Exercise
- In 1 litre rigid vessel at 1 atm and 300 K, N "collision/sec-cm"^(2) o...
Text Solution
|
- 0.5 L of evacuated container is filled by gas upto 1 atm exactly, by c...
Text Solution
|
- At constant pressure mean free path of ideal gas lamda prop T^(x). Hen...
Text Solution
|
- 100 mL of a gas is stored over mercury in mercury manometer at 27^(@)C...
Text Solution
|
- A good vacuum produced in common lab apparatus corresponds to 10^(-6) ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas at 650 Torr occupies a bulb of unknown volune. A certain ...
Text Solution
|
- On litre flask contains air, water vapour and a small amount of liquid...
Text Solution
|
- A diver at a depth of 10 m exhales a bubble of air of volume 24.63 mL....
Text Solution
|
- The gas 'A' decomposes as A rarr B + 5C A partially decomposed gaseo...
Text Solution
|
- A bulb of constant volume is attached to a very thin manometer tube as...
Text Solution
|
- For oxygen at 25^(@)C, the collision diameter is 0.361 nm. What is the...
Text Solution
|
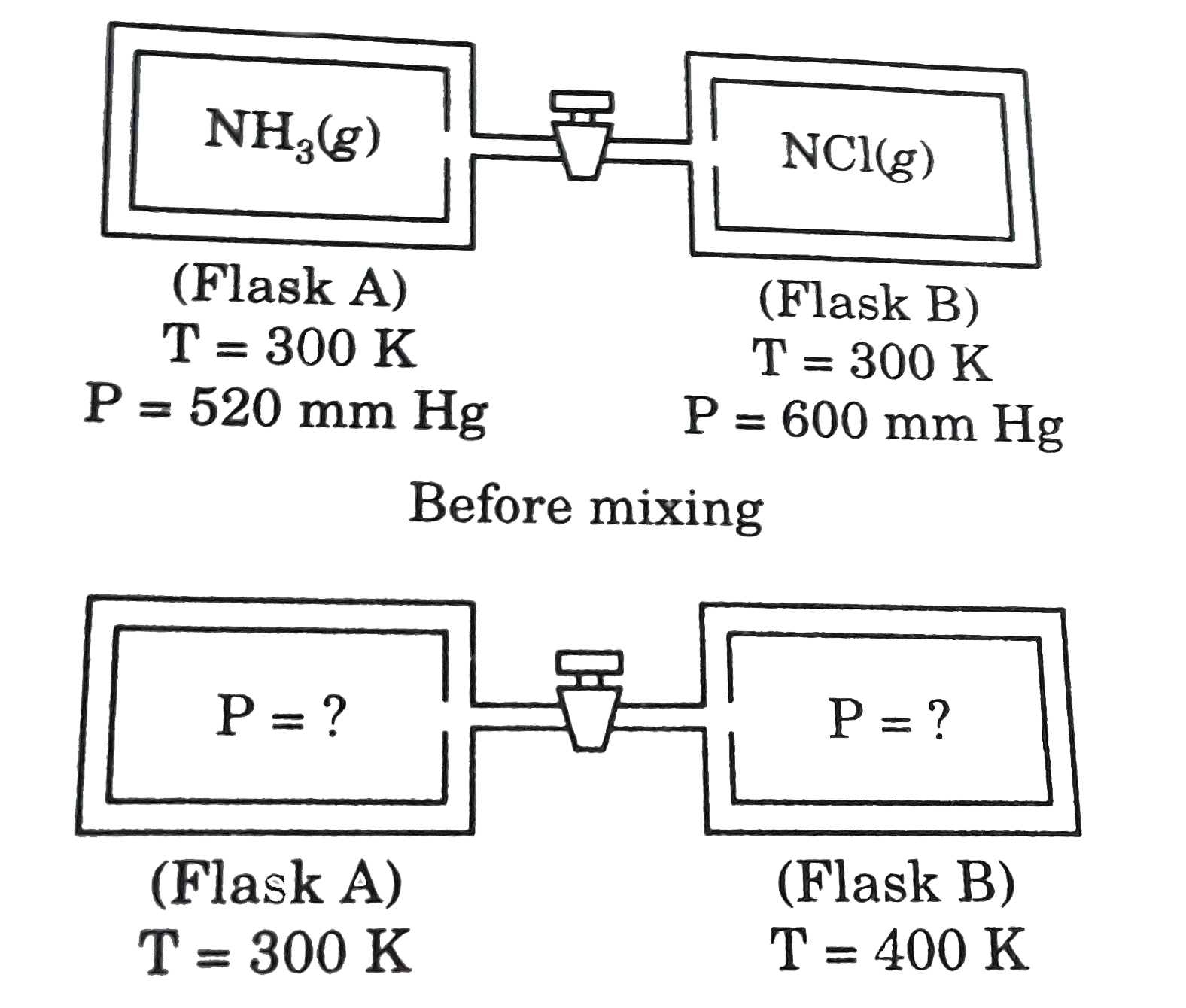
- Two flasks A and B of equal volume containing NH(3) and HCl gases, are...
Text Solution
|
- 22.4 L CH(4) at 1 atm and 273 K was thought to have mass 16 g but when...
Text Solution
|
- Two glass bulbs A and B are connected by a very small tube having a st...
Text Solution
|
- A mixture of H(2),He and O(2) with mass ratio equal to the ratio of th...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mol of a gas is changed from its initial state (15 L, 2 atm) to fina...
Text Solution
|
- PCl(5)(g) density (in g/L) of mixture at 24 atm and 300 K, when PCl(5)...
Text Solution
|
- If the gas in container gas pressure 77 cm of Hg, then calculate the h...
Text Solution
|
- One litre of N(2) and 2 litre of O(2) under identical conditions of T ...
Text Solution
|
- For a real gas, if at critical conditions molar volume of gas is 8.21 ...
Text Solution
|