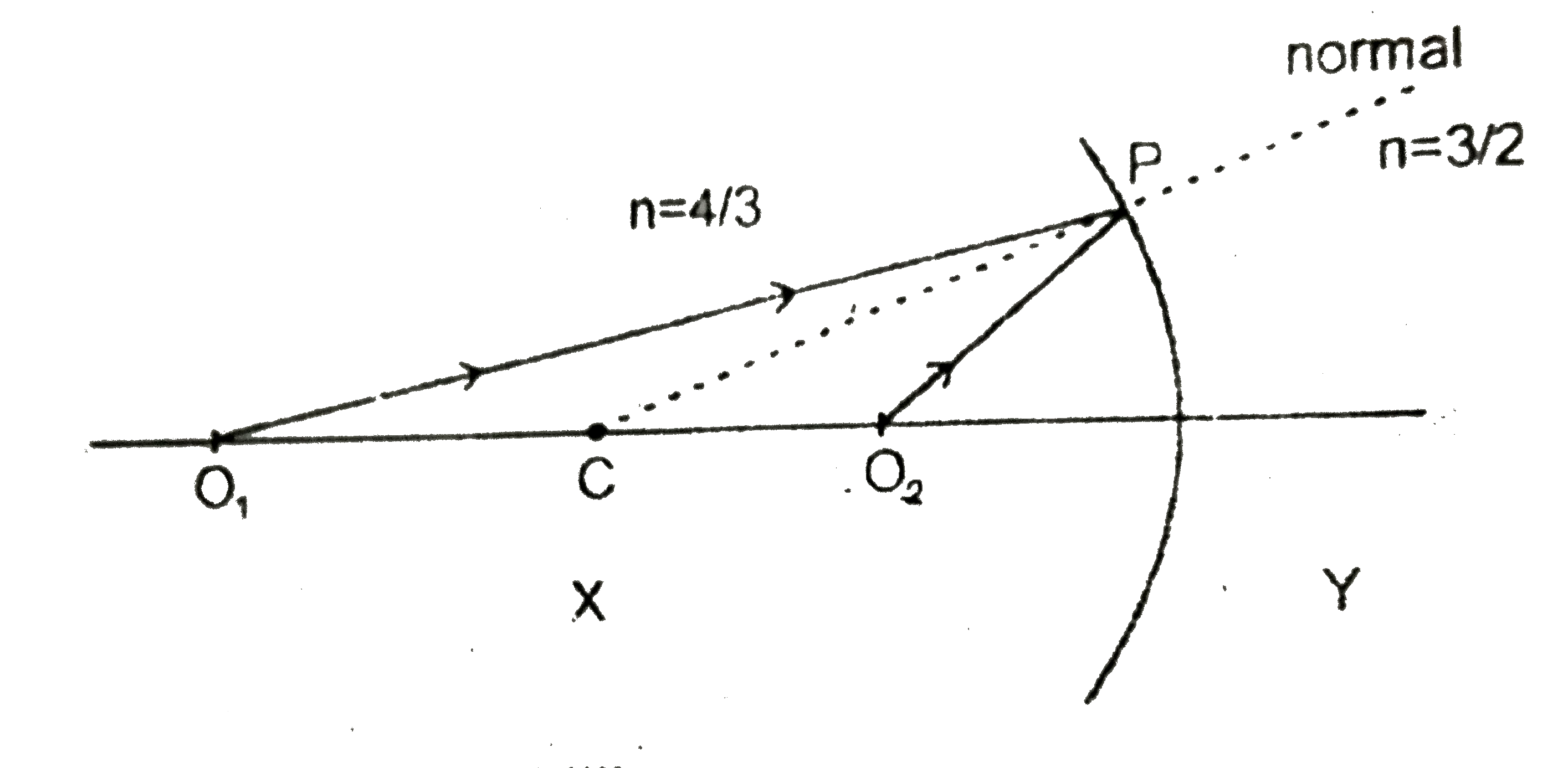
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two...
Text Solution
|
- What curvature must be given to the bounding concave surface of refrac...
Text Solution
|
- A convex refracting surface of radius of curvature 20 cm separates two...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical convex surface separates object and image space of refract...
Text Solution
|
- A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two...
Text Solution
|
- A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 100 cm separates tw...
Text Solution
|
- A convex surface of radius of curvature 40 cm separate two media of re...
Text Solution
|
- वक्रता त्रिज्या 100 सेमी का एक अवतल पृष्ठ अपवर्तनांक 1 cdot 50" तथा "1...
Text Solution
|
- A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two...
Text Solution
|