Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CURRENT
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise APPLICATION TO DAILY LIFE, CONCERN TO BIODIVERSITY|37 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise FILL IN THE BLANKS|8 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION - IV (4 Marks Questions)|16 VideosCHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ESSENTIAL MATERIAL FOR EXAMINATION PURPOSE|1 VideosELECTROMAGNETISM
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise CREATIVE QUESTION FOR NEW MODEL EXAMINATION (SEC-4)|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-ELECTRIC CURRENT-CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDING
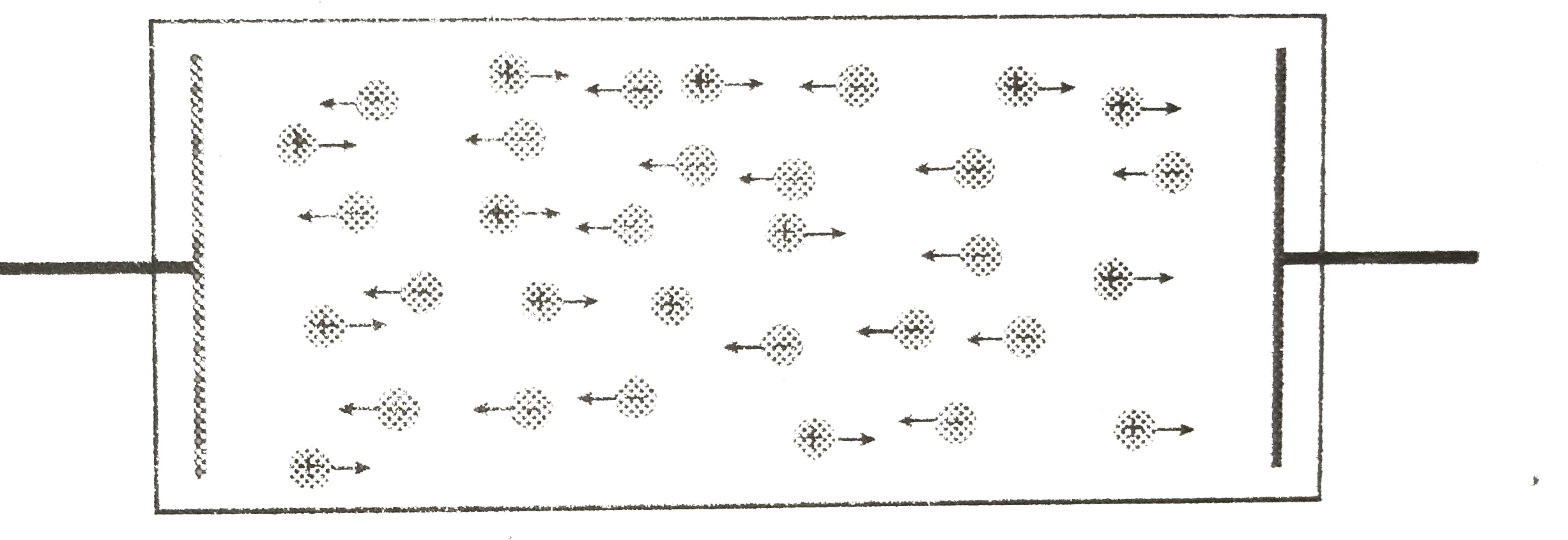
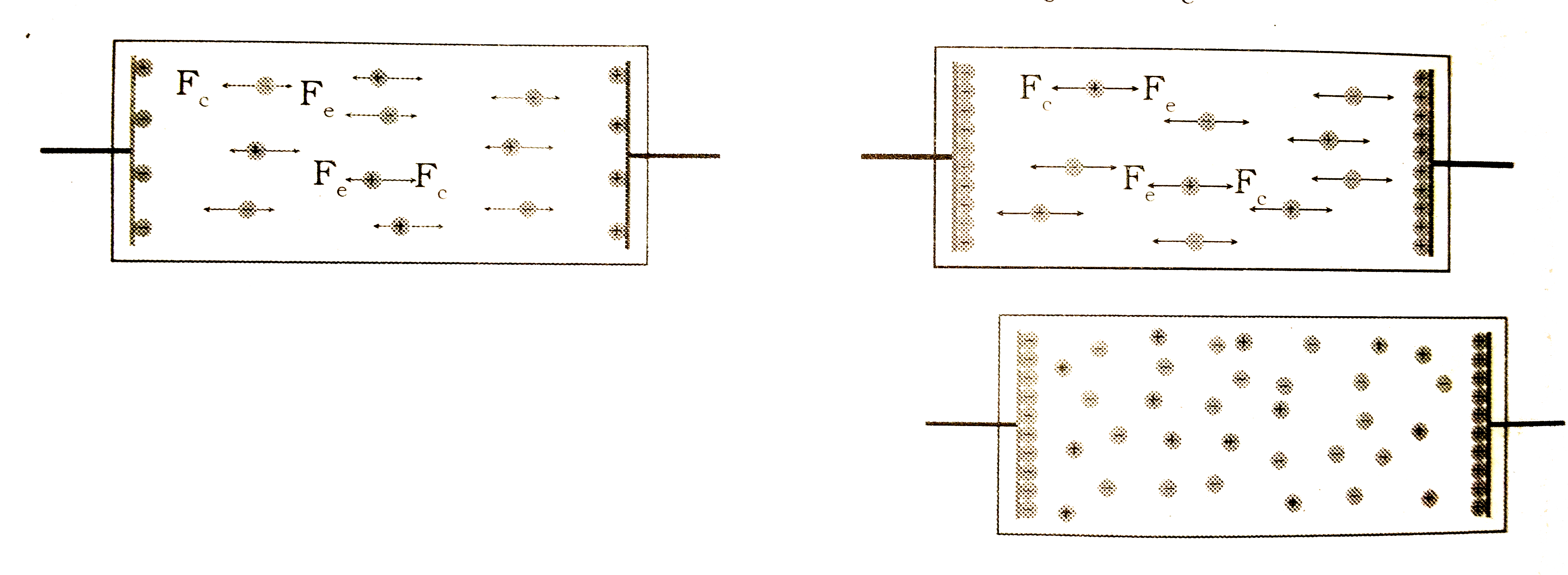
- Explain the lorentz - Drude theory.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the lorentz - Drude theory.
Text Solution
|
- How does a battery work ? Explain.
Text Solution
|
- Write the difference between potential difference and emf.
Text Solution
|
- What do you mean by electric shock ? Explain how it takes place.
Text Solution
|
- "Derive R"=(rhol)/(A).
Text Solution
|
- Derive a formula that shows the relation between resistance length and...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relationship between length of a conductor and its resista...
Text Solution
|
- State Kirchhoff's law for an electrical network. Using these laws dedu...
Text Solution
|
- What is the of 1 KWH in joules ?
Text Solution
|
- What happens when this current (overloading) increases greatly to the ...
Text Solution
|
- Deduce the expression for the equivalent resistance of there resistor ...
Text Solution
|
- " Derive "R=R(1)+R(2)+R(3).
Text Solution
|
- Explain the expression for the equivalient resistance of three resisto...
Text Solution
|
- The second end of a first resistor is connected to first end of second...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the effective resistance when three resistors...
Text Solution
|
- "Derive"(1)/(Rp)=(1)/(R(1))+(1)/(R(2))+(1)/(R(3)).(Resistors in parall...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the effective resistance when three resistors...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the effective resistance when three resistors...
Text Solution
|
- Silver is a better conductor of electricity than copper. Whey do we us...
Text Solution
|