A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GRB PUBLICATION-IONIC EQUILIBRIUM-All Questions
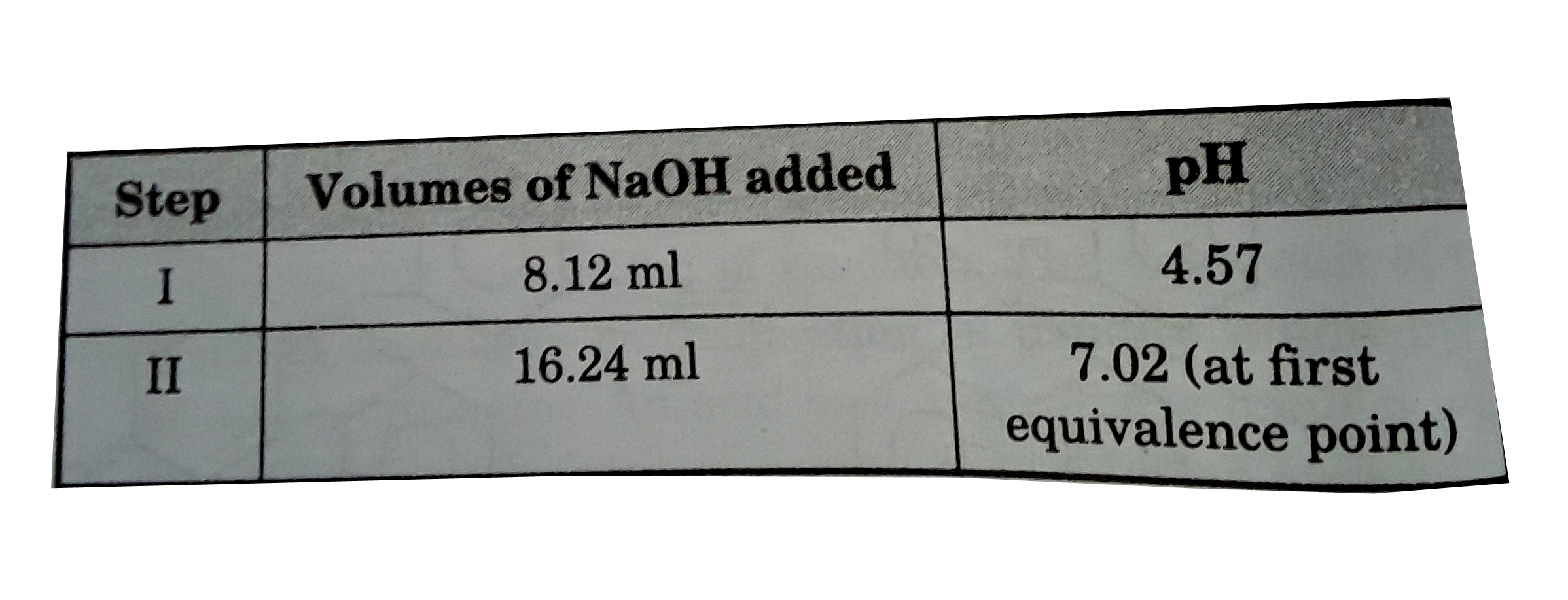
- Following titration method is taken to compute stepwise ionisation con...
Text Solution
|
- Following titration method is taken to compute stepwise ionisation con...
Text Solution
|
- Following titration method is taken to compute stepwise ionisation con...
Text Solution
|
- Acetic acid tends to form dimer due to formation of intermolcular hydr...
Text Solution
|
- Acetic acid tends to form dimer due to formation of intermolcular hydr...
Text Solution
|
- Acetic acid tends to form dimer due to formation of intermolcular hydr...
Text Solution
|
- 100ml of 0.1M H(3)PO(4) is titrated with 0.05 M NaOH solution till 2nd...
Text Solution
|
- 100ml of 0.1M H(3)PO(4) is titrated with 0.05 M NaOH solution till 2nd...
Text Solution
|
- 100ml of 0.1M H(3)PO(4) is titrated with 0.05 M NaOH solution till 2nd...
Text Solution
|
- Selective precipitation of ions in a mixture in the form of salts can ...
Text Solution
|
- Selective precipitation of ions in a mixture in the form of salts can ...
Text Solution
|
- 0.3 g of CH(3) COOH is dissolved in 100ml water to prepare a solution ...
Text Solution
|
- 0.3 g of CH(3) COOH is dissolved in 100ml water to prepare a solution ...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium equation and K(a) values for the three acids are given...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium equation and K(a) values for the three acids are given...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium equation and K(a) values for the three acids are given...
Text Solution
|
- Human blood has a narrow Ph range of 7.3-7.4, which must be maintained...
Text Solution
|
- Human blood has a narrow Ph range of 7.3-7.4, which must be maintained...
Text Solution
|
- Human blood has a narrow Ph range of 7.3-7.4, which must be maintained...
Text Solution
|
- We represent various reagents pictorially such that, The relative...
Text Solution
|