Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
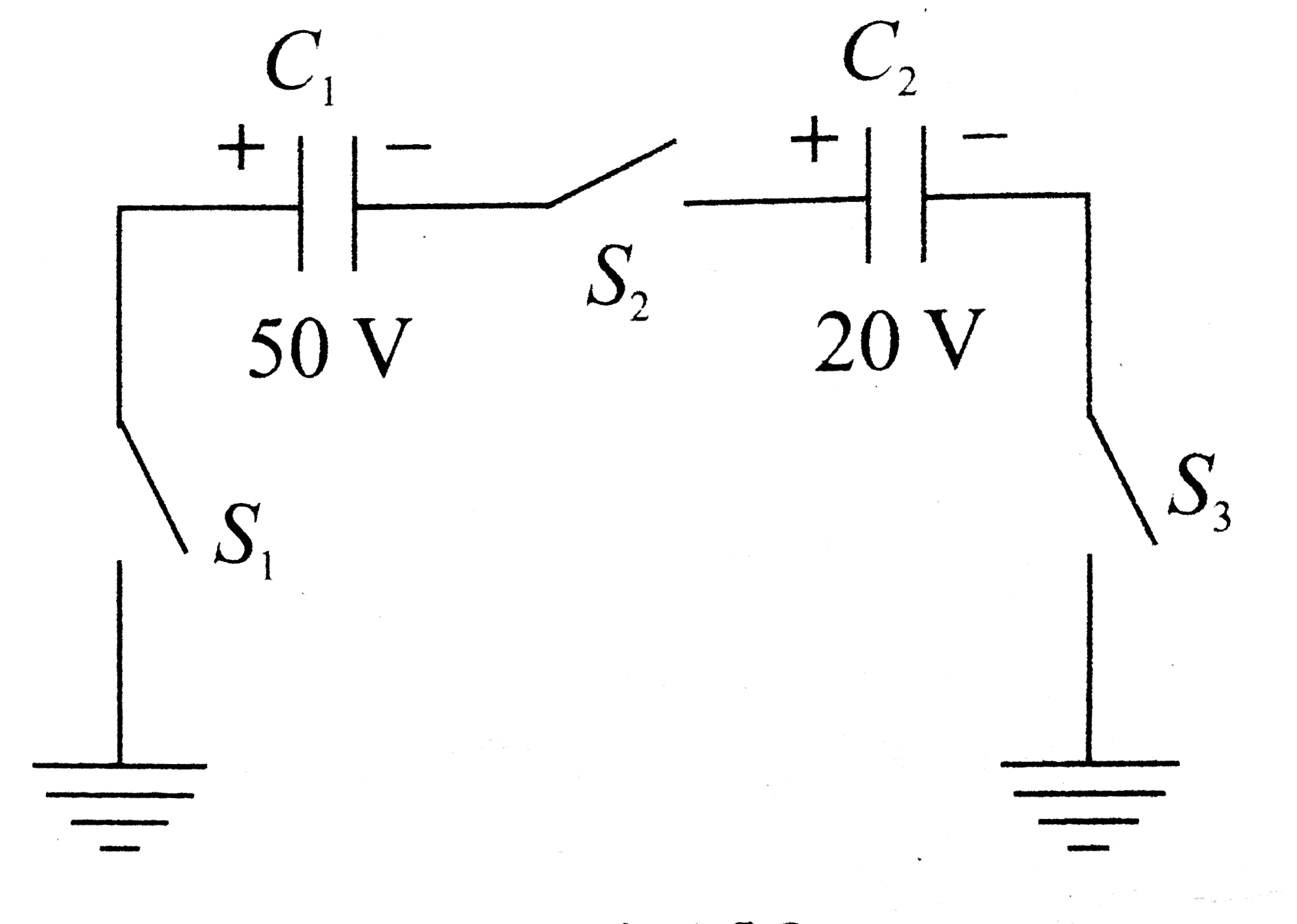
- In the circuit shown, C(1)=C(2)=2 muF. Capacitor C(1) is charged to 50...
Text Solution
|
- For section AB of a circuit shown in , C(1)=1 muF, C(2)=2 muF, E=10 V ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in, C(1)=6 muF, C(2)=3 muF , and battery B=20 V ....
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, C(1)=C(2)=2 muF . Capacitor C(1) is charged to 5...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, C(1) = C(5) = C(6) = 6.0 muF and C(2) = C(3) = C...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors C(1) and C(2) are connected to a battery of 6 V as sho...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in figure C(1)= 1mu F and C(2) = 2 mu F. The capa...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the circuit shown where C(1) = 6 mu F, C(2) = 3 mu F and V=20...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors C(1)"and"C(2) are charged to the same potential V, but ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.